What Is IV Crush in Options
Understanding the key concepts in options trading can provide you with a strategic advantage. Among the crucial terms, you may often encounter the phrase “IV crush”. But what does this imply, and how does it impact your trading approach? This guide will illuminate the intricate details of this phenomenon, emphasizing its role in cryptocurrency options, specifically Bitcoin.
What Is IV Crush in Options Trading?
IV crush stands for “implied volatility crush”. This term has become a cornerstone in the vocabulary of options enthusiasts. It refers to a dramatic drop in implied volatility (IV) following a noteworthy occasion, such as a company's earnings announcement. This abrupt reduction in IV can substantially affect the option prices, typically leading to a rapid devaluation.
In the picture below, you can witness how IV plunges after the earnings announcements (marked by “E” symbol).
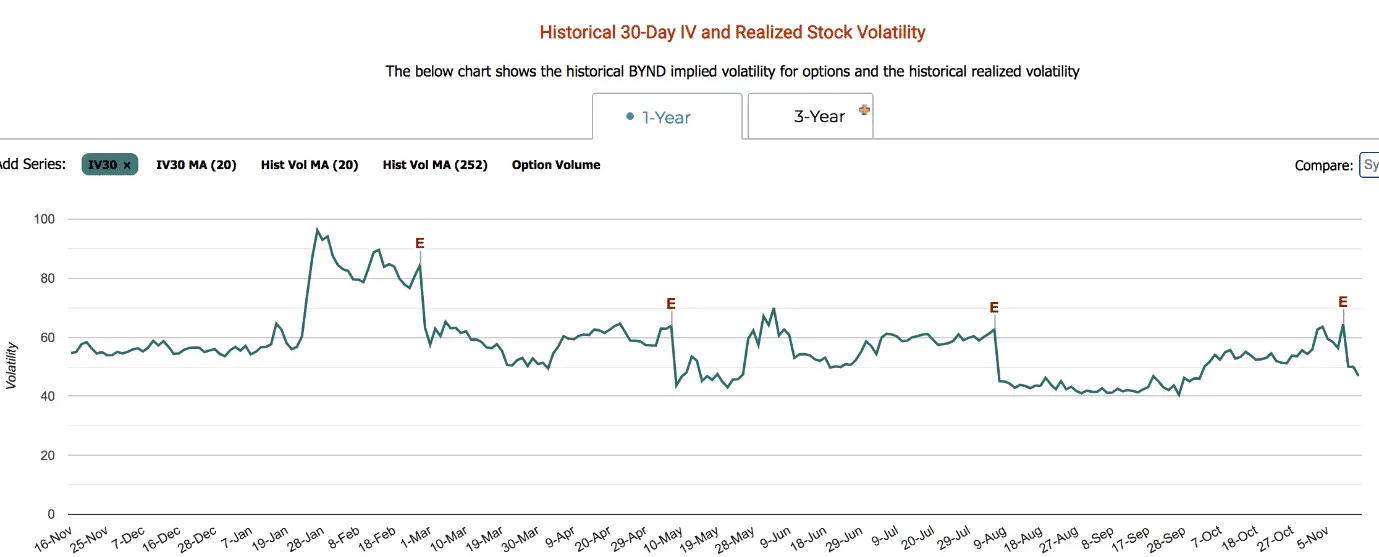
Decoding Implied Volatility: What It Is and How Does It Impact Options Pricing?
In the realm of options trading, understanding the importance of IV crush hinges upon comprehending the fundamental concept of implied volatility (IV). Implied volatility (IV) acts as a pivotal metric, capturing the market’s anticipation of price swings in the underlying asset throughout the option’s lifespan. In essence, it serves as the market’s forward-looking projection of future volatility, providing valuable insights into the market's sentiment and expectations.

When it comes to options pricing, implied volatility plays a pivotal role. High levels of IV can lead to inflated option premiums due to the increased risk associated with the underlying asset's potential price movement. Conversely, a drop in IV can deflate option prices, leaving option holders in a less than ideal position.
How Is Implied Move Calculated?
One of the essential skills for an options speculator is the ability to calculate the implied move. This is the projections of the anticipated price fluctuation in the underlying asset, derived from the option's price. Essentially, it offers a glimpse into the potential future value of the asset, empowering traders with valuable insights.
Here's how you may estimate the implied move, using the implied volatility of an at-the-money (ATM) straddle (it combines a call and a put option with identical strike prices). The formula for calculating the implied move is relatively straightforward:
Implied Move = (Option Straddle Cost / Underlying Asset Price) * 100%
Using this formula, traders can gauge the expected percentage change in the asset's price based on the cost of the option.
Remember that this is an estimate of the implied move and not a guarantee. It's also worth noting that the actual outcome may be influenced by several factors, such as major upcoming news events.
Examples of Volatility Related to the Federal Reserve (Fed) Key Interest Rate
Volatility in financial markets often increases leading up to major economic announcements. This is particularly true for announcements related to the Federal Reserve (FED) key interest rate, which can significantly impact financial markets.
Here's an example:
Consider an upcoming FED meeting where a change in the key rate is expected. As the meeting draws near, the prevailing uncertainty surrounding it outcomes grows, triggering heightened levels of implied volatility (IV) within the options market. This surge in IV stems from options traders’ anticipation of amplified price fluctuations in the underlying assets (like stocks, indices, or commodities) based on the FED's decision.
For Bitcoin, the relationship might be less direct but still significant. If the FED raises rates, it could strengthen the U.S. dollar, which might put downward pressure on Bitcoin prices. If traders anticipate this, they could drive up the IV for Bitcoin options ahead of the FED meeting. Conversely, if the FED is expected to lower rates, this could weaken the U.S. dollar and potentially boost Bitcoin prices, which could also increase the IV as traders anticipate the potential for upside.
Hypothetical Trade to Demonstrate IV crush
Let's say you're an options' trader, and you're looking at Bitcoin options ahead of a FED meeting where a rate hike is expected. The IV on these options is high because traders are expecting the FED's decision to cause significant price swings in Bitcoin.
You decide to sell a Bitcoin call option, betting that the IV is overstated and will fall after the FED announcement. This strategy is known as selling volatility or being “short vega”.
The FED meeting happens, and they raise rates as expected. However, the Bitcoin price doesn't react as strongly as the options market anticipated. This causes the IV of the Bitcoin options to drop significantly—a phenomenon known as IV crush.
Since you sold the option when IV was high, you benefit from this IV crush. The option you sold is now worth significantly less, allowing you to buy it back at a lower price and profit from the difference.
The Pitfalls of IV Crush
Now, let's discuss the pitfalls of IV crush. In fact, there are many nuances:
- Erosion of option value. The main pitfall of IV crush is that it can cause a substantial value depletion for option holders. Following a significant event, a sharp decline in implied volatility can occur, leading to a diminished value of the option. This reduction happens even if the price of the underlying security remains unchanged. Consequently, option holders may face undesirable losses, emphasizing the impact of IV crush on their positions.
- Difficulty to predict. It's hard to foretell when a significant event will occur that will cause the implied volatility to drop. This makes it challenging for option holders to prepare for and potentially avoid the effects of an IV crush.
- Difficulty in timing trades. Traders may try to take advantage of an IV crush by selling options before the implied volatility decreases. However, timing these trades can be difficult. If you sell too early, you may miss out on potential gains from an increase in the price of the underlying security. If you sell too late, the IV crush may have already occurred, and you may incur a loss.
- False expectations. Sometimes, traders may overestimate the effect of an event on a security's price, leading to inflated implied volatility. When the event happens and the security's price doesn't change as much as expected, implied volatility can plummet, leading to an IV crush.
- Risk vs. Reward. Options boasting high IV frequently exhibit high premiums, making them more appealing to sellers. However, the potential reward must be carefully weighed against the inherent risk associated with a substantial adverse movement in the underlying security's price.
How to Avoid IV Crush
IV crush can have a devastating impact on option holders, particularly those who purchase options ahead of significant events. However, there are strategies to mitigate the negative effects.
Firstly, becoming cognizant of the event calendar is crucial. Being aware of upcoming events can help traders avoid purchasing options when IV is at its peak. Secondly, purchasing options when implied volatility is low can be a wise move. This strategy ensures you are not paying an inflated premium for the option, thus minimizing potential losses from an IV crush.
Recognizing the intricate interplay between options pricing and implied volatility unlocks the pathway to success. As market uncertainty surges, the demand for options contracts intensifies, which in turn inflates their extrinsic value, leading to an elevated implied volatility.
However, as the event concludes, the market transitions from a state of ambiguous information to one of general information. This transition typically triggers in a rapid decline in implied volatility, giving rise to the phenomenon of IV crush. By aligning strategies with this nuanced relationship, traders can navigate the disruptive terrain and harness the potential hidden within.
IV Crush Following Company Earnings
A striking IV crush example can be observed following company earnings announcements. These events are a time of high uncertainty, as market participants eagerly anticipate the results. This anticipation often leads to increased trading activity, pushing up the implied volatility of options.
In the example below, you can see that implied volatility falls after each Apple earnings announcement, despite a significant change in price.
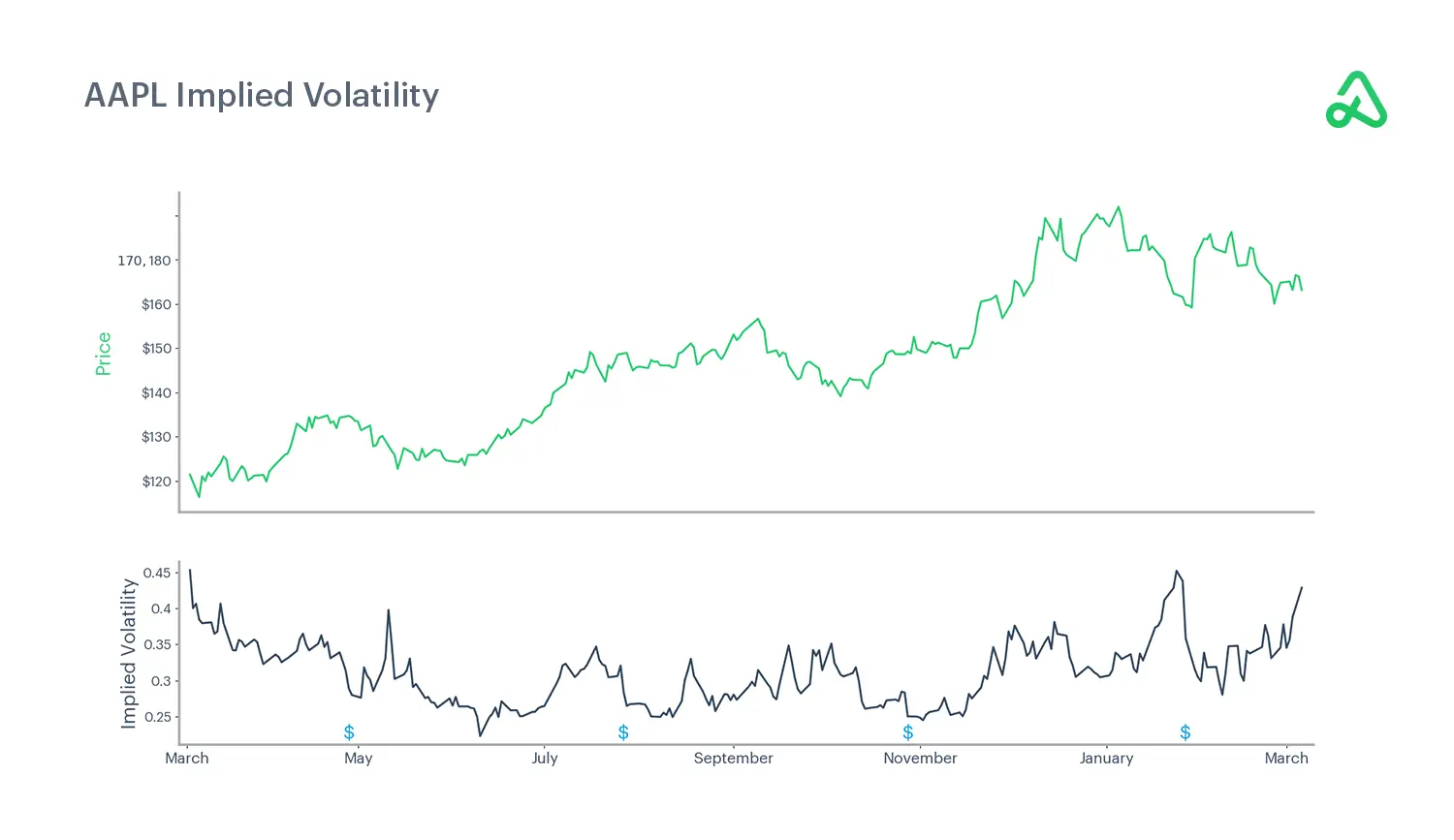
Investors who expect earnings to exceed expectations may choose to acquire call options, aiming to capitalize on the forthcoming announcement. Conversely, those anticipating lower than expected earnings may purchase put options. This combined activity of call and put buyers contributes to an increase in volatility as they anticipate an unforeseen outcome in earnings.
However, once the earnings are announced, these trades are often swiftly closed. The rapid selling activity decreases volatility, leading to an IV crush. This process results in a significant decline in the option's value, regardless of whether the earnings met, exceeded, or fell short of expectations.
Profiting From IV Crush Explained
While IV crush can pose significant challenges to option buyers, it can also present opportunities for savvy traders. One strategy for capitalizing on IV crush is to sell options around earnings announcements. This approach involves selling options when implied volatility is high, allowing the seller to collect inflated premiums.
It's worth noting that selling options can be risky. However, considering that approximately 80% of options expire worthless, sellers often stand to benefit. Importantly, this strategy should be employed judiciously, and only by traders who fully understand the risks involved.
Strategies to Exploit IV Crush: The Opportunity in Volatility
So, how can one turn the threat of IV crush into an opportunity? The key lies in understanding the dynamics of implied volatility and exploiting it to your advantage. Here are a few strategies that savvy traders can employ to take advantage of IV crush:
- Sell options before significant events. This approach involves selling options when implied volatility is high, allowing the seller to collect inflated premiums. After the event, the decline in IV can lead to a decrease in the value of the option, which can be beneficial for the seller.
-
Trade volatility itself through instruments like VIX options and futures. These specialized instruments enable traders to bet on the future trajectory of volatility itself, rather than on the price fluctuations of a specific underlying asset.
Leverage sophisticated options strategies like iron condors or straddles. These strategic approaches can effectively harness the advantages of a decline in implied volatility, making them particularly suitable in the context of earnings announcements and similar events.
Remember, while these strategies can be profitable, they also carry risks. Always ensure you understand the trade and its potential outcomes before entering into it.
Sellers Beware of Gamma Risk
When aiming to sell options with the intention of benefiting from IV crush, it becomes vital to maintain awareness of gamma risk. This concept represents the rate at which the option's delta changes, reflecting its price sensitivity concerning the underlying asset's price. As the option nears its maturity date, gamma risk possesses the potential to result in substantial losses for those selling options.
IV Crush and Bitcoin: Managing Volatility Expectations
Here are some tips which will help traders to successfully manage volatility expectations in Bitcoin options trading:
- Stay informed about market events that impact Bitcoin's volatility.
- Understand IV crush and its effect on option prices.
- Analyze historical volatility patterns to anticipate future changes.
- Utilize a range of options strategies, such as spreads or hedging techniques.
- Monitor implied volatility levels and consider buying or selling options accordingly.
- Implement risk management measures such as setting clear parameters and diversifying your portfolio.
Remember to thoroughly understand the risks involved in options trading and consider seeking professional advice.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing IV crush is critical when trading options. Whether you're dealing with Bitcoin, other cryptocurrencies, or any other volatile underlying asset, IV crush remains an integral part of risk management and a strategic element in decision-making processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is IV Crush Meaning in Options?
An IV crush (implied volatility crush) denotes a pronounced decrease in the level of implied volatility for an underlying asset, resulting in a subsequent depreciation in options' prices.
How Can Traders Take Advantage of IV crush?
Traders can exploit IV crush by strategically selling options during periods implied volatility is high and subsequently buying them back when IV crush occurs, resulting in a subsequent decline in option prices.
How Does IV crush Affect Cryptocurrency Options?
In the realm of cryptocurrency trading, including Bitcoin, IV crush can lead to significant decreases in the prices of options, thereby affecting the potential profitability of various options trading strategies.
How Can Traders Avoid the Negative Impact of IV crush?
To mitigate the adverse impacts of IV crush, traders have the opportunity to incorporate a range of strategies, including spreads, into their trading routine. Moreover, they can leverage the potential of IV crush by strategically selling options during periods characterized by elevated levels of implied volatility and subsequently buying them back when the crush materializes.
What Is IV Crush in Stocks?
"IV Crush" is a term used in options trading. It refers to a sudden plunge of an options contract's price, triggered by a drastic decrease in implied volatility, often in the wake of a key event like an earnings release. Although it involves stocks indirectly (given that options are contracts to trade stocks), the term itself is specific to options trading and isn't commonly used in direct stock trading.
*This communication is intended as strictly informational, and nothing herein constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy, sell, or retain any specific product, security or investment, or to utilise or refrain from utilising any particular service. The use of the products and services referred to herein may be subject to certain limitations in specific jurisdictions. This communication does not constitute and shall under no circumstances be deemed to constitute investment advice. This communication is not intended to constitute a public offering of securities within the meaning of any applicable legislation.




