What Does It Mean to Burn Crypto?
What does “burn” mean in crypto? At its core, burning crypto refers to the deliberate act of making a certain amount of cryptocurrency permanently inaccessible.
This action is executed by sending tokens or coins to a designated address, often termed a “burn address”, from which they can never be retrieved.
This process, while seemingly straightforward, has profound implications for the cryptocurrency's ecosystem, its value, and its stakeholders. The act of burning helps to manage the supply and demand of an asset. If it concerns the supply and demand, you may wonder does coin burn increase the price of the remaining coins? The answer is yes! However, the coin burn does more than that, which we will discuss in this article.
Key Takeaways
- Burning crypto refers to the intentional act of making certain cryptocurrency tokens permanently inaccessible, typically by sending them to a “burn address”.
- The process involves permanently removing tokens from the circulating supply, leading to increased scarcity of the remaining tokens. This can potentially drive up the token's value if demand remains constant.
- Projects burn crypto to demonstrate commitment, manage token supply, protect against spam, increase coin value, maintain stablecoin stability, and show long-term dedication.
- Crypto burn reduces the supply of the token/coin, meaning that the token value may eventually change. It also has technical ramifications, affecting aspects like transaction prioritization and consensus mechanisms.
- Burning has been a part of the crypto landscape for a while, initially addressing unsold ICO tokens. Its reasons and methods have evolved over time, especially with the rise of DeFi platforms.
- While burning can lead to potential value appreciation and increased trust, it also poses concerns about irreversible actions, potential for manipulation, and long-term supply issues.
- Every burn event is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and preventing false claims about token reductions.
How Does Burning Crypto Work?
What is burning crypto? At its core, the process involves intentional and permanent removal of tokens from the available circulating supply. It is achieved by sending tokens to a specific cryptographic address, often referred to as the “burn address”. This address is unique in that it lacks a corresponding private key, ensuring that tokens sent there can never be moved or accessed by anyone.
The immediate consequence of this action is a reduction in the total number of tokens in circulation. As the circulating supply diminishes, each remaining token's relative scarcity increases. In economic terms, assuming demand remains constant, this heightened scarcity can exert upward pressure on the token's price, as there are fewer tokens available for the same level of demand.
Furthermore, the act of burning is deeply rooted in the principles of blockchain technology. Every transaction, including token burns, is recorded on the blockchain. Thus, a permanent, immutable record of the burn event is ensured. Anyone can verify the integrity of the burn by examining the blockchain ledger, ensuring that the stated number of tokens have indeed been removed from circulation. The illustration below is an example of an address for burning coins on Ethereum.
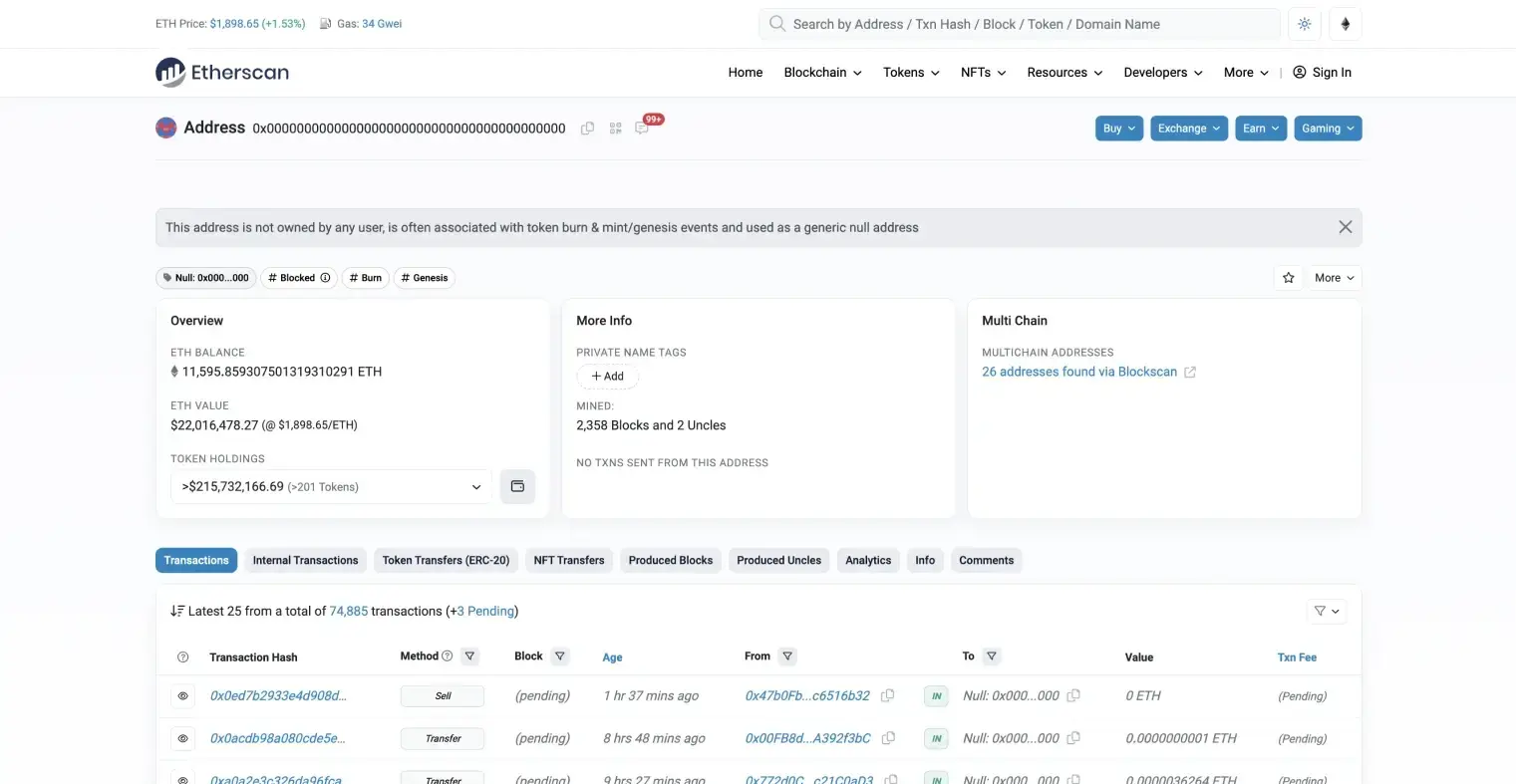
This level of transparency and verifiability adds an element of trust. It ensures that projects or entities cannot make false claims about token burns without the evidence on the blockchain.
In addition to its economic implications, burning also has technical ramifications. Depending on the cryptocurrency's underlying protocol, burning can affect various aspects, from transaction prioritization to consensus mechanisms.
Here is a typical sequence of a token burn event:
- Announcement: projects usually start by announcing their intention to conduct a token burn. This announcement will detail the number of tokens to be burned, the reason for the burn, and the date of the event.
- Preparation: before the burn, developers prepare by setting up the necessary code changes. They identify the tokens to be burned, often those in the project's reserve or those bought back from the open market.
- Execution: on the decided date, the tokens are sent to the burn address. The address is public, and the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency.
- Verification: after the burn, anyone can verify the transaction by checking the blockchain. The burn address will show the tokens, but without a private key, they are inaccessible and effectively removed from circulation.
- Post-burn report: many projects release a detailed report after the burn event. This report will confirm the number of tokens burned and may provide insights into the project's future plans or the expected impact of the burn on the token's economics.
- Monitoring and feedback: after the burn, the project team monitors the token's performance in the market, gathers feedback from the community, and makes decisions about potential future burns or other strategic moves.
By following this sequence, projects ensure that the token burn is conducted transparently, effectively, and in the best interests of the community and stakeholders.
Reasons for Burning Crypto
Burning crypto is also a way for projects to demonstrate their commitment to a robust economic model. By actively managing their token supply, projects can signal to investors that they are committed to maintaining, if not increasing, the token's value. This can be especially important for projects in their early stages, where investor confidence can play a crucial role in the project's success.
Furthermore, as the crypto industry matures, we're seeing more innovative uses of burning. Some projects are now tying burning mechanisms to specific actions or milestones. For instance, a project might commit to burning a certain number of tokens every time a specific goal is achieved, aligning the interests of the project and its token holders.
1. As a Consensus Mechanism
Consensus is a crucial component in the world of blockchain and cryptocurrency. Burning crypto can serve as a unique consensus mechanism. In certain systems, instead of miners receiving new tokens as rewards, they earn transaction fees from the tokens that are “burned”.
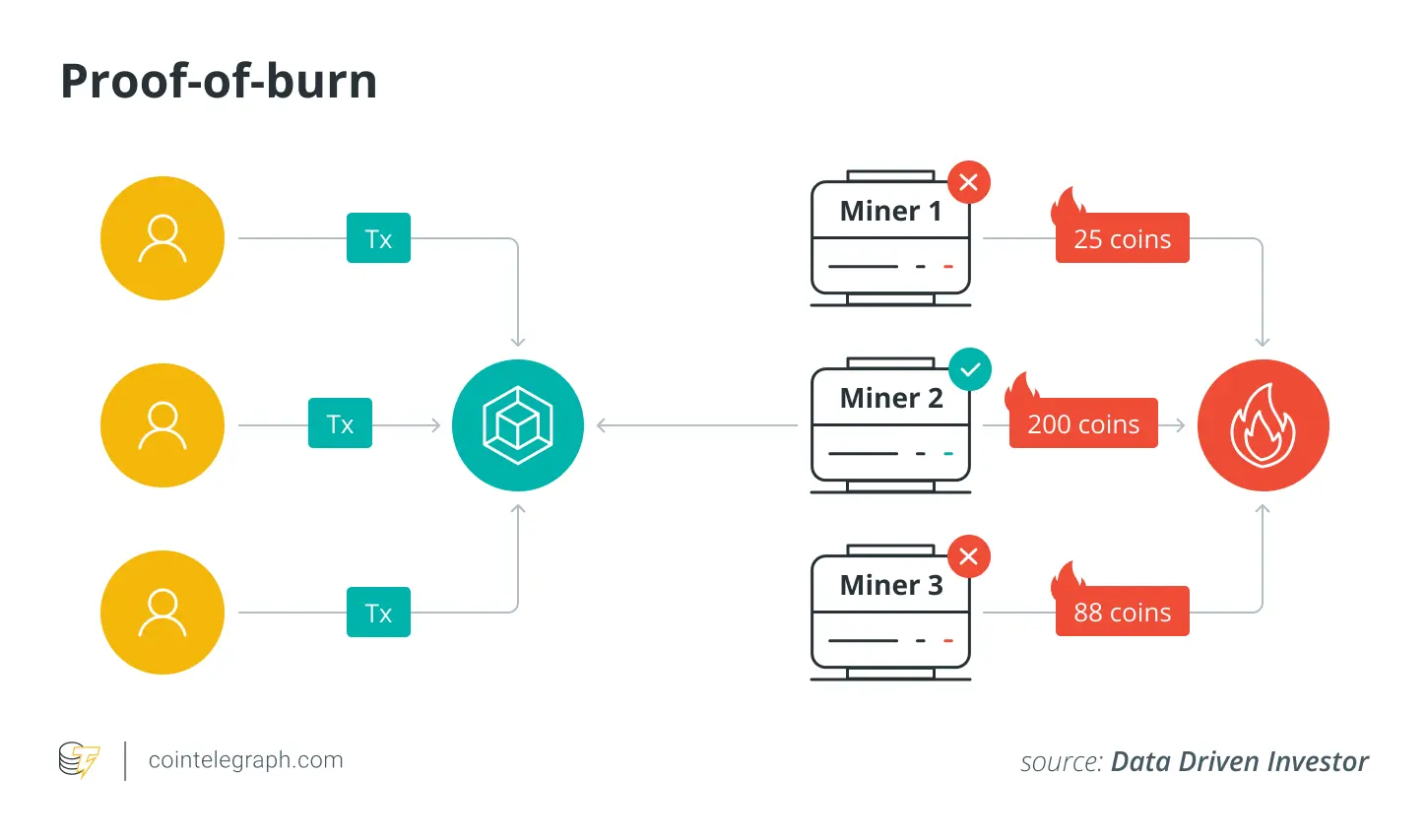
This approach can align the interests of miners and users, ensuring the long-term security and viability of the blockchain.
2. To Protect Against Spam
Blockchains, while offering transparency and security, can be vulnerable to spam or malicious attacks. Spam in blockchain terms refers to unnecessary transactions that can overload the network. To counteract this, some networks introduce a mechanism where users burn a small amount of crypto for certain actions. One example of such networks is Ethereum, which uses EIP-1559 burning mechanism.
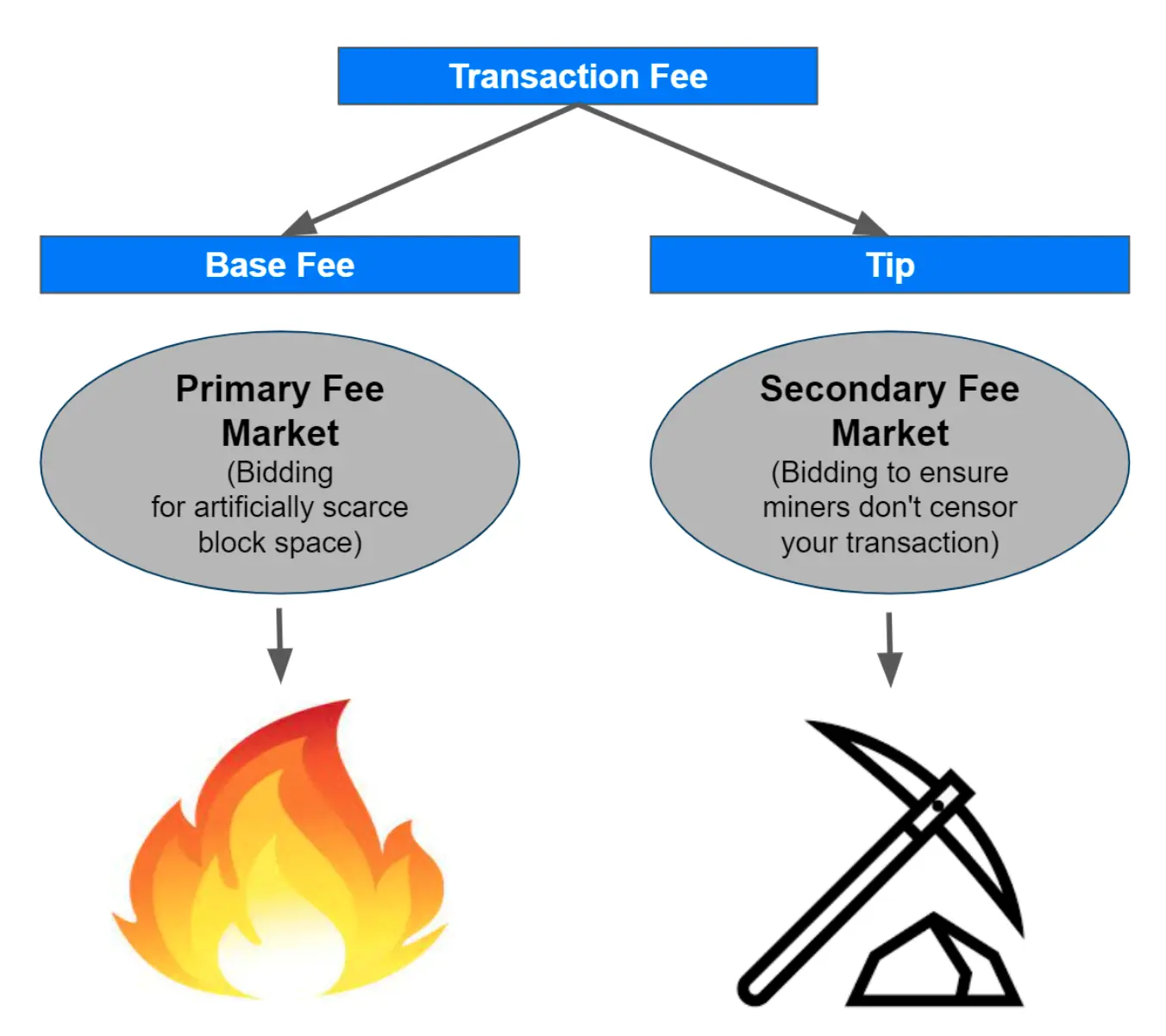
Here's a condensed overview of the main benefits of token burn in terms of network protection:
- Deterrence: a burn fee attached to transactions makes it costly for attackers to flood the network, deterring spam.
- Filtering genuine transactions: genuine users willing to pay the fee for valid transactions are prioritized, ensuring the network remains functional.
- Dynamic fees: some networks adjust burn fees based on activity, increasing them during high congestion to further deter spam.
- Efficient resource use: by curbing spam, computational networks ensure resources are used efficiently, maintaining speed and reliability.
- Enhanced security: burn fees make attacks expensive, reinforcing network security.
3. To Increase a Coin's Value
One of the most cited reasons for burning crypto is to influence its value. By intentionally reducing the supply of a cryptocurrency, its inherent scarcity can potentially rise.
This artificial scarcity can, in turn, drive up demand and possibly the coin's value. For investors and stakeholders, this can be a promising sign of the cryptocurrency's future potential.
4. To Keep Stablecoins Stable
Stablecoins have emerged as a bridge between traditional fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies. Pegged to assets like the US dollar, stablecoins aim to offer the best of both worlds – the stability of fiat and the flexibility of crypto. Burning plays a crucial role in maintaining this peg. If the market price of a stablecoin drifts below its pegged value, it suggests a surplus supply in the market. In such scenarios, burning some stablecoins reduces the supply, which can help push the price back up towards its pegged value.
5. As a Sign of Long-Term Commitment
Token burning is also a potent symbol of a project's dedication to its vision and longevity. By willingly reducing the circulating supply, project developers or companies send a clear message about their confidence in the project's future and their intent to enhance its value.
For instance, consider the case of the crypto exchange Binance. Periodically, Binance commits to burning a portion of its native BNB tokens. This act is not just a mechanism to regulate the token's supply but also a testament to Binance's commitment to its platform and its token holders. Every burn event is accompanied by an official announcement, detailing the number of tokens burned and the reasons behind the decision. Such transparent actions bolster trust among its vast user base, reinforcing the belief that the platform is invested in the long-term value and utility of BNB.
In essence, token burning can serve as a strategic move, not just in terms of economics but also in terms of public relations and trust-building. For investors and stakeholders, it's a reassuring sign, indicating that the project is here to stay and is taking active steps to ensure its sustained relevance and growth.
6. To Promote Mining Balance
Cryptocurrency mining is an energy-intensive process. In ecosystems where mining plays a pivotal role, tokens might be burned to ensure that mining remains profitable. By adjusting the rewards miners receive through burning, networks can maintain a healthy balance of miners, ensuring network security and transaction processing efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Burning Crypto
Every strategic action has its benefits and drawbacks, and burning crypto is no exception. Understanding these pros and cons can offer insights into the broader implications of such actions in the cryptocurrency domain.
Pros of Burning Crypto
- Value appreciation: a primary benefit of burning crypto is the potential appreciation in the value of the remaining tokens. As supply decreases and if demand remains constant or increases, the value of each token can rise.
- Deterrence against spam: by requiring users to burn a small amount of tokens for certain actions, networks can deter spam or malicious activities, ensuring network security.
- Signaling commitment: burning tokens can be perceived as a sign of a project's long-term commitment, fostering trust among investors and stakeholders.
Cons of Burning Crypto
- Irreversible action: the act of burning is final. Once tokens are burned, they are permanently removed from circulation, and there's no way to retrieve or reintroduce them.
- Potential for manipulation: if not conducted transparently, burning events can be perceived as attempts to artificially manipulate the market or the token's value.
- Supply concerns: over time, excessive burning can lead to concerns about the token's total supply, potentially affecting its utility and demand.
Different Types of Coin Burning
Coin burning is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the objectives and the underlying cryptocurrency's protocol, different methods of burning can be employed.
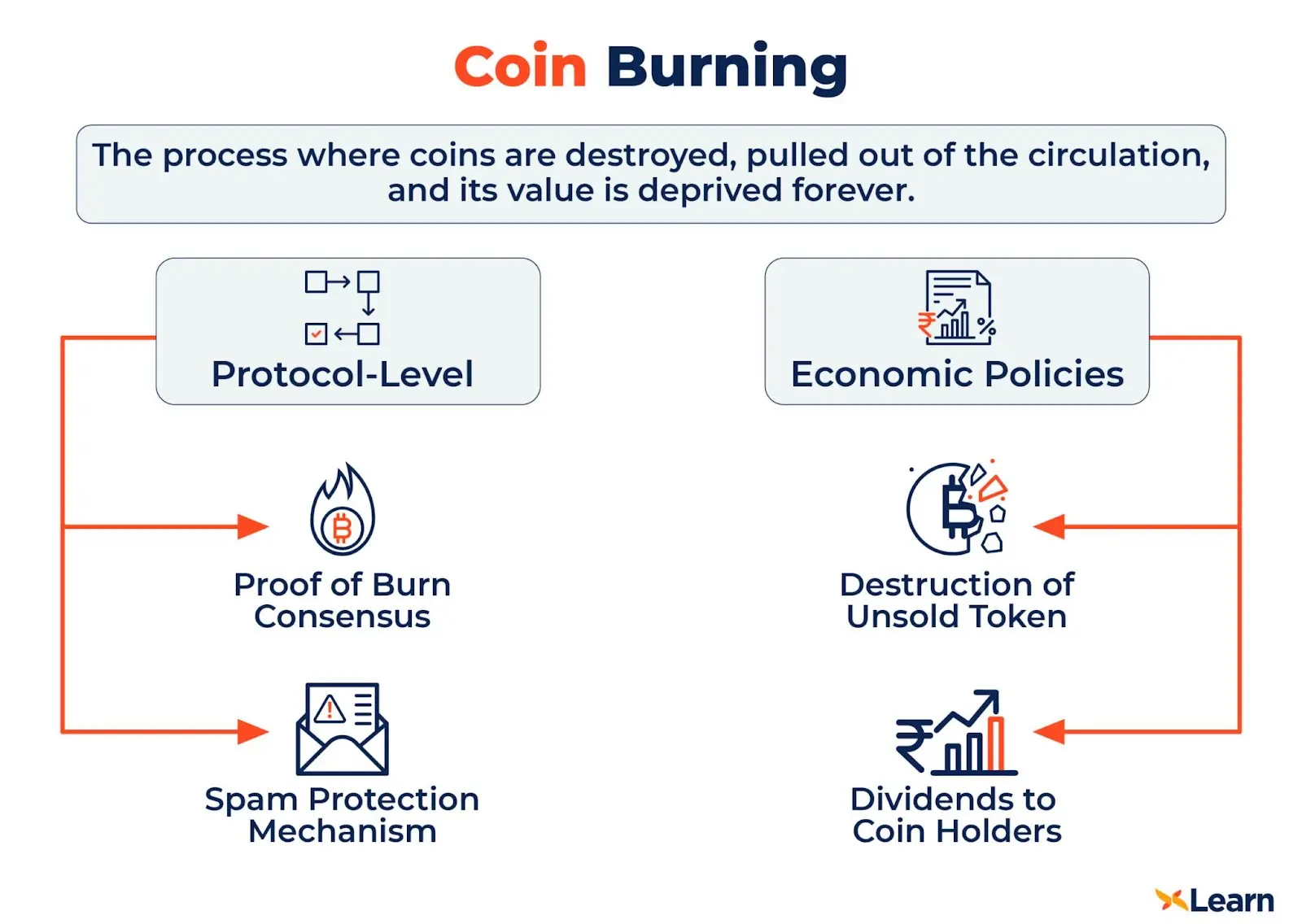
1. Coin Burning at the Protocol Level
Some cryptocurrencies have inherent burning mechanisms built directly into their protocols. This type of burning is automated and occurs based on predefined rules or triggers within the system. For instance, a certain percentage of transaction fees might be burned automatically with every transaction.
The examples of such cryptocurrencies are BNB, EOS, ETH, and others.
2. Coin Burning as Economic Policy
This approach is more discretionary. Here, the project's leaders or governing body decide to burn coins as a strategic economic decision. This could be to manage token supply, respond to market conditions, or even as a corrective measure after unforeseen events.
3. Coin Burning in Lieu of Dividends
Some projects opt for a unique approach where, instead of distributing dividends or rewards to holders, they burn tokens. The idea is that by reducing the supply, the value of the remaining tokens might increase, benefiting all holders indirectly.
How Does Burning Affect A Cryptocurrency's Value?
With the reduction of the total supply of a cryptocurrency, its scarcity increases. If demand remains constant or even grows, this heightened scarcity can lead to an increase in the token's value. However, it's essential to understand that while burning can influence a token's value, it's not the sole determinant. The broader market sentiment, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and global economic conditions also play pivotal roles.
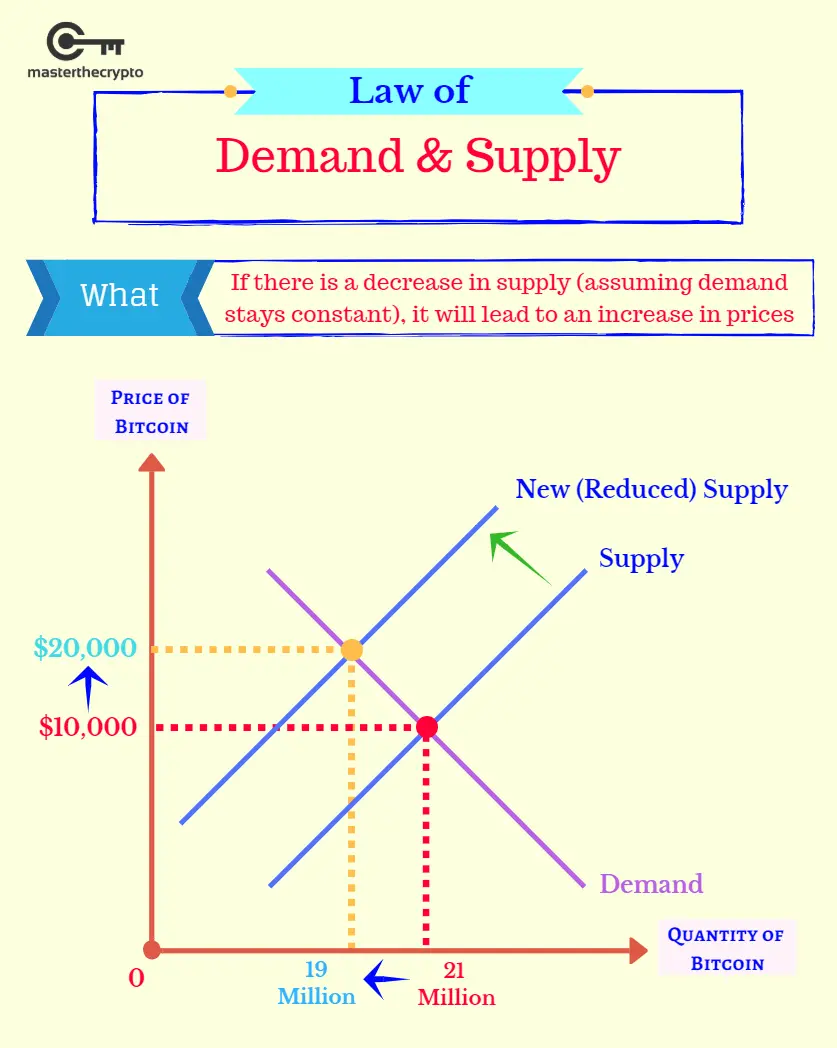
Moreover, the act of burning can be perceived as a positive signal by the market. It can be seen as a demonstration of a project's commitment to maintaining a stable token value or even increasing it. This can, in turn, boost investor confidence and potentially drive further demand for the token, leading to a positive feedback loop of increasing value.
History of Crypto Burn
The concept of burning tokens has been a part of the landscape for quite some time. Initially, it was a mechanism to address unsold tokens after Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). Projects would burn unsold tokens to ensure they didn't flood the market, which could depress the token's value. Over time, the reasons for burning evolved.
Different projects have made token burning a regular event. By committing to burn a certain amount of their native coins regularly, they aim to reduce its overall supply over time, potentially boosting its value.
In recent years, with the rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms and various other blockchain-based projects, the reasons and methods for burning tokens have expanded. Today, burning is not just a tool for value appreciation but also a mechanism for governance, spam prevention, and more.
Conclusion
Burning crypto tokens is a strategic decision in the cryptocurrency realm, aimed at permanently removing a portion of tokens from circulation. This isn't merely about supply reduction; it's a multifaceted approach with varied implications.
Burning signifies a project's commitment to its vision, enhancing stakeholder value. It boosts investor trust in a volatile market. Economically, by altering the circulating supply, burning can influence token scarcity and potentially its value. This is vital for stablecoins aiming to maintain their asset peg.
Transparency is another advantage. Each burn event is blockchain-recorded, ensuring verifiability and countering false claims about token reductions.
As the crypto world evolves, burning remains a tool for projects to navigate changing conditions and regulations. It's a testament to adaptability and foresight.
In conclusion, burning tokens will persist as a key strategy in the crypto domain, shaping project directions and market dynamics in the foreseeable future.
FAQ
What Is a Crypto Burn?
“Burning” is a term used to describe the process of removing cryptos from the circulation. A certain amount of assets is sent to an inaccessible address, never to be used again. This practice can amplify a token's rarity and, in turn, its potential worth.
Is Burning Cryptocurrency Good or Bad?
Burning cryptocurrency can be both beneficial and detrimental. While it can lead to value appreciation and increased trust in a project, it can also raise concerns about the long-term supply and potential market manipulation.
How to Burn Crypto Tokens?
Tokens are burned by sending them to an inaccessible or "burn" address. Once sent to this address, they are permanently removed from circulation and cannot be retrieved.
Why Do Companies Burn Cryptocurrency?
Companies burn cryptocurrency for various reasons, from managing token supply to signaling commitment and more. It's a strategic decision that can influence the project's trajectory and its token's value.
Does Coin Burning Increase Its Price?
Yes, burning crypto can potentially increase its value. By reducing the supply and creating scarcity, the demand for the remaining tokens can rise, leading to an increase in value. However, various factors, including market sentiment and overall demand, influence this outcome.
*This communication is intended as strictly informational, and nothing herein constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy, sell, or retain any specific product, security or investment, or to utilise or refrain from utilising any particular service. The use of the products and services referred to herein may be subject to certain limitations in specific jurisdictions. This communication does not constitute and shall under no circumstances be deemed to constitute investment advice. This communication is not intended to constitute a public offering of securities within the meaning of any applicable legislation.




