Unconfirmed Blockchain Transaction: What Is It & How To Avoid Them
A blockchain represents a continuously growing sequence of records, referred to as blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography. Ordinarily, every block contains a cryptographic hash pertaining to the preceding block, a timestamp, and data related to transactions.
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data, providing a robust platform for crypto like Bitcoin. However, as with any technology, there are certain challenges that users may encounter. One such challenge is the occurrence of unconfirmed blockchain transactions.
This article explores the intricacies of unconfirmed blockchain operations, exploring their characteristics, reasons for occurrence, and potential solutions to mitigate these issues.
Key Takeaways
- Transactions on the blockchain that have not yet received confirmation are the payments that are waiting to be added to a block.
- These transactions are visible to the network but lack confirmation on the blockchain.
- They are vulnerable to double-spending, where the same funds are spent more than once.
- Network congestion, low transaction fees, and transaction prioritization by miners can lead to pending transactions.
- Methods to fix or recover pending operation include increasing the transaction fee, using mechanisms like RBF, and efficient off-chain solutions or layer 2 protocols.
What is an Unconfirmed Bitcoin Transaction?
Before delving into the specifics of an unconfirmed BTC transaction, it is essential to cover the overall mechanics of a BTC transaction.
A BTC transaction is a record on the blockchain. It contains the sender's and recipient's (output and input) wallet addresses, the amount of Bitcoin to be transferred from the sender to the recipient, the quantity of confirmations and other information.
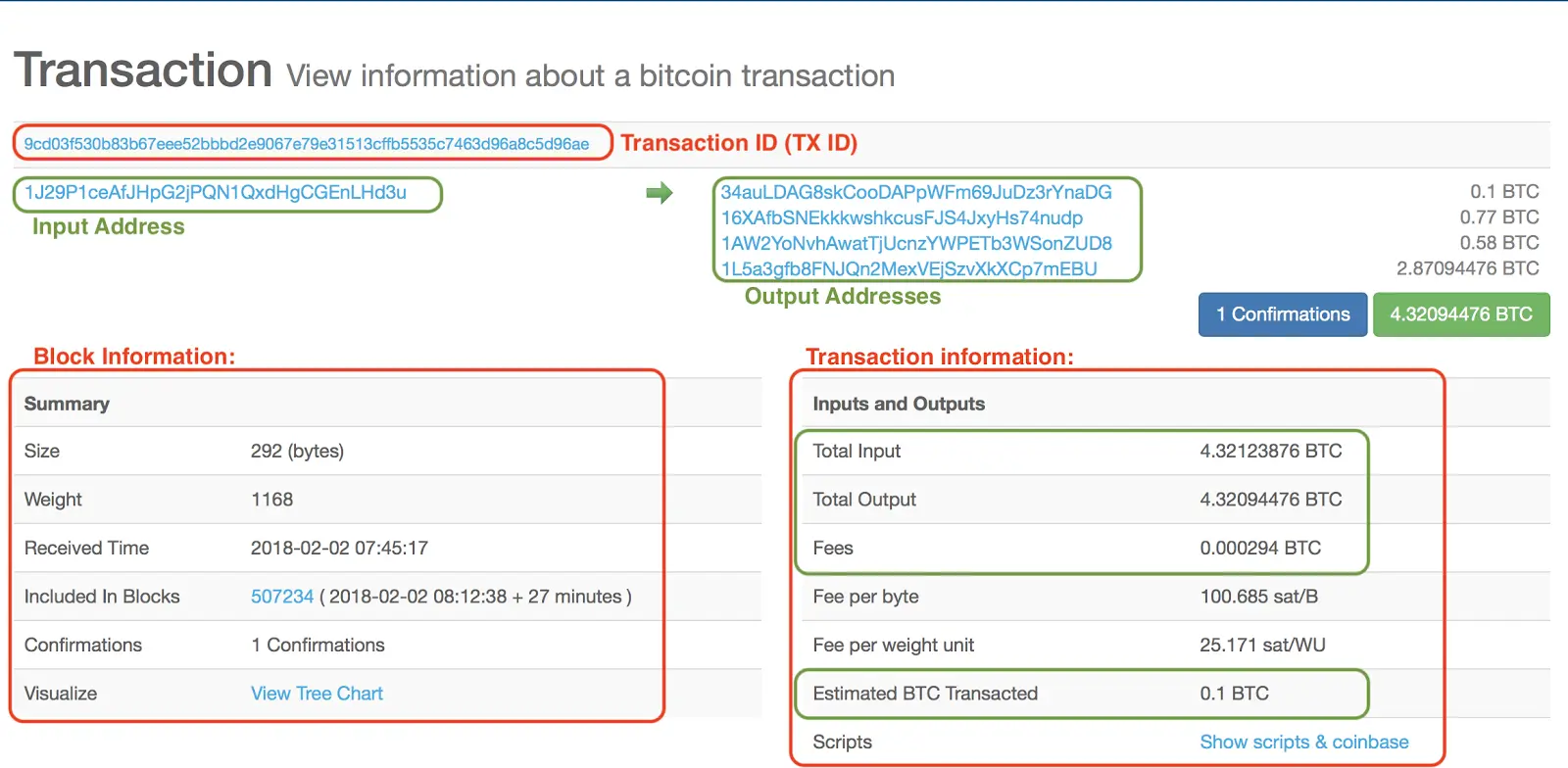
This operation is sent to the Bitcoin network for validation and inclusion in the blockchain. In essence, a transaction is a way of transferring value from one Bitcoin wallet to another, and it serves as the fundamental building block of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Now, an unconfirmed bitcoin transaction is an operation that has been broadcast to the network but has not become a part of a block yet. This means that it has not yet been confirmed by the network and is not yet incorporated into the blockchain.
Typically, BTC transactions awaiting confirmation are stored in a sort of waiting list — a mempool (memory pool) — until they are picked up by miners and added to a block.
The mempool acts as a holding area for all the operations that are waiting to be picked up by miners. Thus, miners choose mempool transactions, validate them, and then include them in a new block. Once a transaction has been verified and included in a block, it is deemed confirmed and subsequently becomes an immutable component of the blockchain.
Characteristics of Blockchain Unconfirmed Transaction
A transaction is initiated in the Bitcoin network undergoes a series of steps before it is verified and subsequently added to the blockchain. However, it may take some time for it to be fully verified. Below, we explore the characteristics that are crucial to understanding the dynamics of blockchain operations.
Lack of Confirmation on the Blockchain
Unprocessed transactions are yet to receive confirmation to become recorded on a blockchain. For a BTC transfer to be processed, at least 1 confirmation is required. Until that, there is no guarantee that the transfer won’t be reversed. This lack of confirmation can leave the transaction susceptible to certain vulnerabilities, such as double-spending.
Pending Status and Transaction Visibility
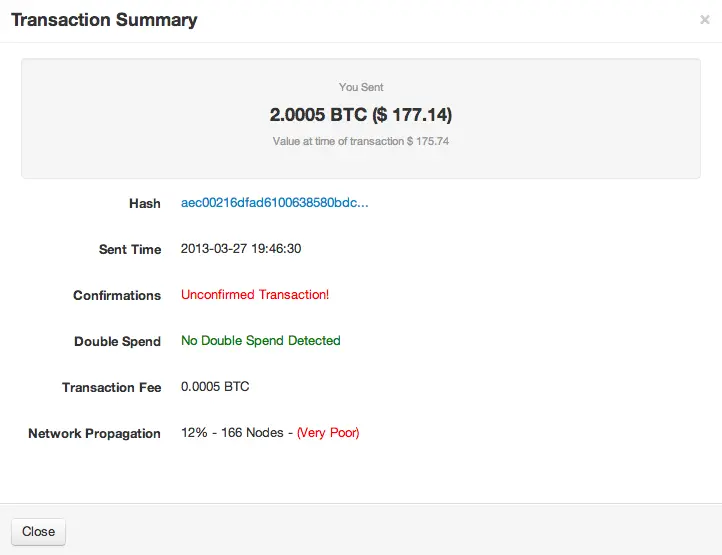
Despite their lack of confirmation, unconfirmed payments are still visible to the network. They exist in a pending status, awaiting their inclusion in a block by the miners. For instance, here’s how you will see the pending status on a Trezor wallet:

At the same time, the pending status is also visible to everyone on any blockchain explorer:
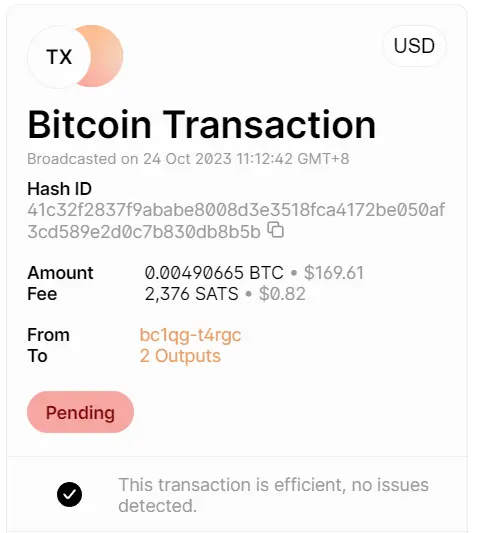
This visibility is a crucial aspect of blockchain operations, as it allows users to track the status of their transaction in real-time. Moreover, it ensures transparency in the network, as all participants can see such details as the sender's and recipient's wallet addresses and the amount of Bitcoin being transferred.
Vulnerability to Double-Spending
One of the significant risks associated with pending transactions is their vulnerability to double-spending. Double-spending occurs when the same funds are spent more than once before the transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain.
Since pending operations are not yet part of the blockchain, there is a possibility that the sender could attempt to spend the same funds again, leading to potential fraud. Blockchain technology, with its consensus mechanisms and decentralized nature, aims to prevent double-spending by ensuring that once a payment is confirmed, it cannot be altered or reversed, and the funds cannot be spent again.
What Is a Bitcoin Transaction Fee?
Before being incorporated into a block, all transactions are processed and confirmed by miners. For their efforts, miners are rewarded with transaction fees.
The fee is not fixed and can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the transaction and the current network conditions. The size of an operation is measured in bytes, and the fee is usually denoted in satoshis per byte (a satoshi is the smallest unit of Bitcoin, equivalent to 0.00000001 BTC).
When the network is congested with a high volume of transactions, users may opt to pay a higher fee. Thus, miners will be incentivized to process the payment promptly.
Various services provide the data about the current average BTC transaction fee, for instance Ycharts:
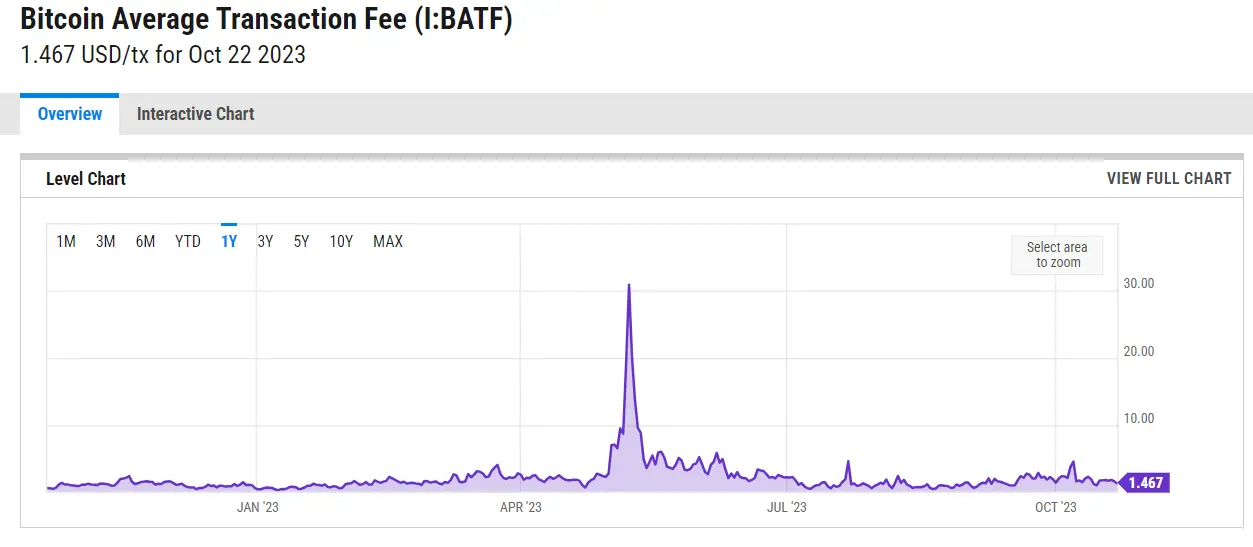
It is important to note that the transaction fee is paid to the miners and not to the Bitcoin network itself. The fee acts as a reward for the miners, compensating them for the computational power and resources they expend in processing transactions and maintaining the network's security.
Why Bitcoin Transactions May Remain Unconfirmed
When a user initiates a Bitcoin transaction, it is broadcast to the network and waits in the mempool as a mempool unconfirmed transaction until a miner picks it up and includes it in a block. However, there are instances when a mempool unconfirmed transaction may remain pending for a longer period, and several factors can contribute to this delay.
The data about the number of the transactions waiting in the mempool is transparent and available on different resources, such as blockchain.com.
Network Congestion and High Transaction Volume
One of the primary reasons why Bitcoin transactions may remain unconfirmed is due to network congestion and high transaction volume. The Bitcoin network can handle a limited quantity of transactions per block, and when there is a surge in the quantity of transactions, it can lead to congestion, similar to traffic congestion on a highway.
In such scenarios, the transactions that are added to a block are determined by the miners, who prioritize transactions based on various factors, including the transaction fee. This congestion can result in delays, and some transactions may remain pending until the congestion clears.
Low Transaction Fees
Another factor that can contribute to zero-confirmation transactions is low fees. Miners are incentivized to include transactions with higher fees in a block because it is more profitable for them. Therefore, if a user pays a too low fee, there is a possibility that miners may choose not to include the transaction in a block, resulting in the transaction remaining pending. This is why it is important for users to be mindful of the transaction fee they are willing to pay, especially during times of network congestion.
Transaction Prioritization
Transaction prioritization is directly linked to the transaction fee. Higher-fee transactions are more likely to be included in a block. This is because miners are rewarded with the transaction fees for the transactions they include in a block. Therefore, transactions with higher fees are more attractive to miners and are more likely to be confirmed faster.
Confirmation Policies
It is important to note that different wallets and exchanges have their own set of policies regarding the quantity of confirmations required before a transaction is deemed complete or final. This number can vary significantly from one service to another, and it often depends on factors such as the size of the transaction and the level of security desired by the service.

For instance, smaller transactions may only necessitate one or two confirmations, while larger transactions, which are inherently more risky, might require six or more confirmations to be considered secure and final. While 1 confirmation is sufficient for an amount less than $1,000, the transactions with larger amount demand more than 3 confirmations.
This discrepancy in confirmation requirements can lead to varying waiting times for transactions to be fully confirmed, depending on the specific policies of the wallet or exchange service being utilized.
How to Check Bitcoin Transaction Time?
The process of checking the time of a BTC transaction is straightforward and can be accomplished with the aid of a blockchain explorer. A blockchain explorer serves as a search engine for the blockchain, providing users with the ability to look up specific transactions and view pertinent details, such as the time the transaction was incorporated into a block.
An explorer can be found on a searching engine. Most popular options include Blockchain.com, BTCScan, Blockstream, and BTC.com.
This functionality is particularly beneficial for users who wish to monitor the status of their transactions and verify that they have been successfully confirmed and added to the blockchain. By utilizing a blockchain explorer, users can gain peace of mind knowing that their transactions have been processed as expected.
How to Speed Up Bitcoin Transactions?
Accelerating a BTC transaction can be achieved through a couple of methods.
- First, by opting to pay a higher fee. Thus, the transaction becomes more enticing to miners and there is a higher chance of the transaction being incorporated into the forthcoming block. In order to set a fee high enough, one can check the current average BTC fee first.
- Second, utilizing a wallet or exchange known for its expedited confirmation times can also contribute to a faster transaction process. Some services provide an option for priority processing, albeit at a premium fee, which can significantly reduce the time taken for a transaction to be confirmed.
- And third, by using a Bitcoin transaction accelerator — a service speeding the transaction confirmation time. Such services charge a fee for transaction prioritization. Some notable accelerators include Binance Pool and ViaBTC.
Even though they are considered to be the most reliable accelerators in the industry, it is still strongly recommended to conduct research about them on your own. Also, be aware of the fishing websites which mimic the above-mentioned resources.
These methods collectively serve as effective means to expedite BTC payments, ensuring a more efficient and timely process.
How do I Fix or Recover Unconfirmed Bitcoin Transactions?
When a BTC transaction awaits confirmation, it can be a source of frustration and concern. However, there are several methods that can be employed to address this issue and expedite the confirmation process.
Higher Transaction Fees
One effective strategy to enhance the likelihood of a transaction being included in the next block is to increase the transaction fee. This process, often referred to as “fee bumping”, makes the transaction more appealing to miners, thereby improving its chances of being processed promptly. The higher fee serves as an incentive for miners to prioritize the transaction over others with lower fees.
Some wallets, such as Blockstream Green, allow for increasing the fee already after the transaction is sent to the network.
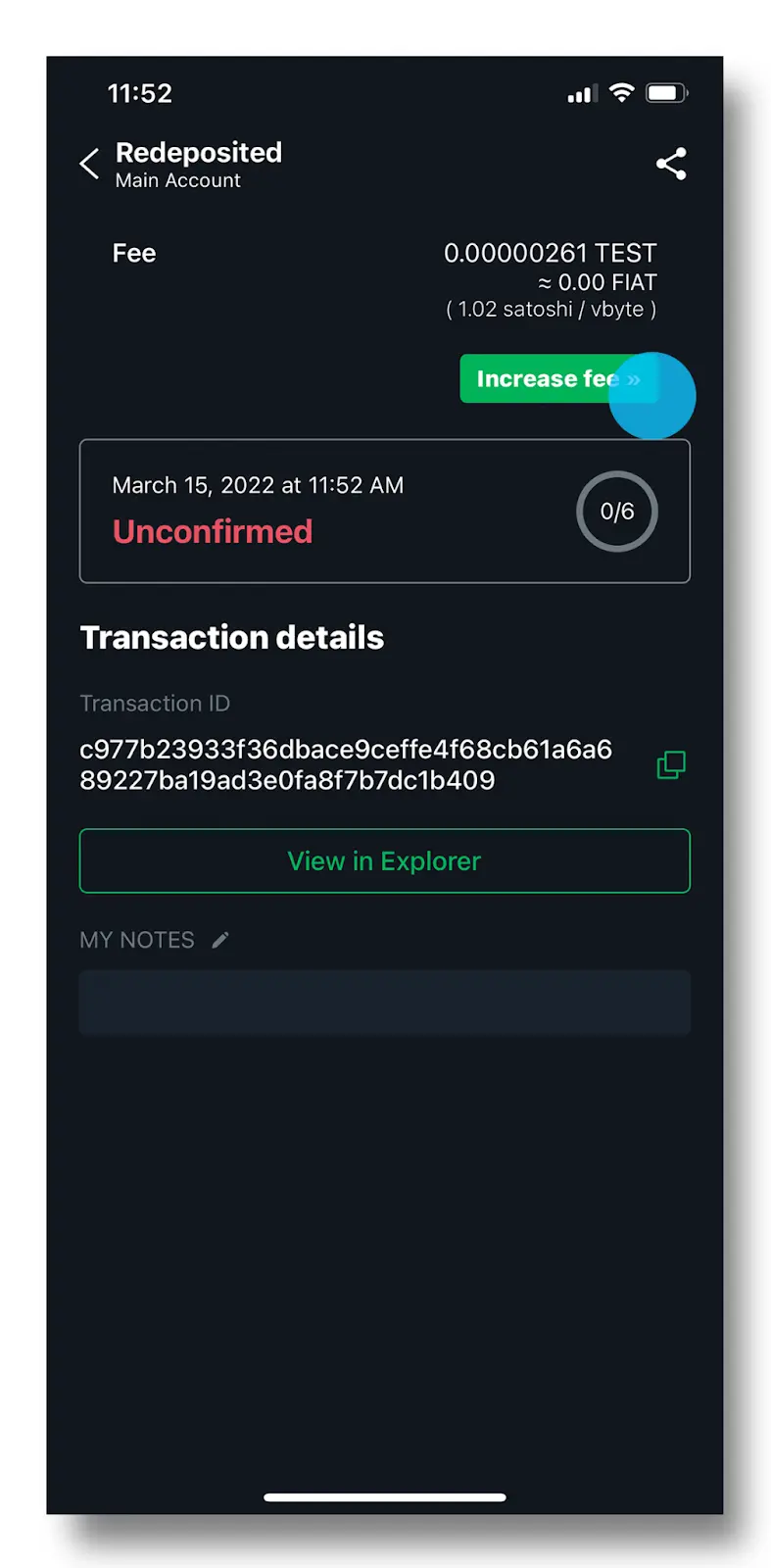
Transaction Replacement Mechanisms
Transaction replacement mechanisms, such as the Replace-by-Fee (RBF) protocol, provide a valuable solution for users facing pending transactions due to low fees. By utilizing these mechanisms, users can initiate a new transaction with a higher fee, effectively replacing the original unprocessed transaction.
As you can see in the picture below, on the left, the RBF function can be enabled by default in some wallets:
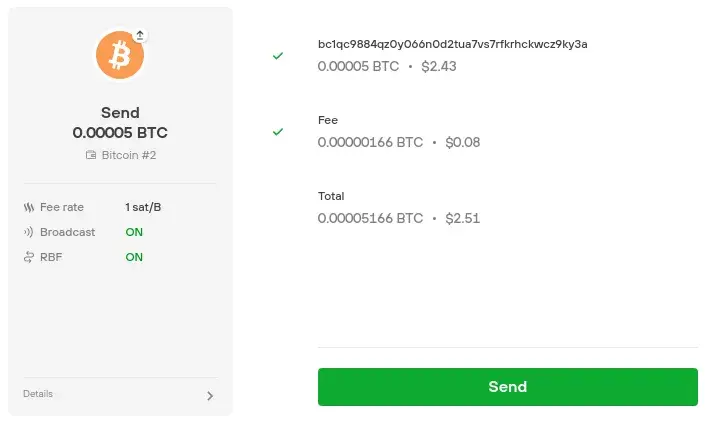
Others require the user to manually enable the transaction replacement ability:
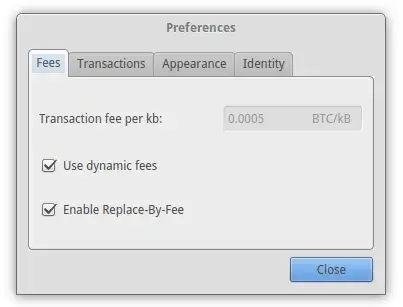
This higher fee serves as an incentive for miners, increasing the likelihood of the new transaction being included in the next block, thus expediting the confirmation process. It is important for users to verify if their wallet supports the RBF protocol, and be mindful that not all miners may choose to support this feature. Additionally, users should be cautious of the potential risks associated with transaction replacement, such as the possibility of accidentally paying twice if not executed correctly.
Off-Chain Solutions and Layer 2 Protocols
Off-chain solutions and layer 2 protocols solutions facilitate the processing of transactions outside the blockchain. Thereby, they alleviate congestion and accelerating the confirmation process. After these transactions are settled off the main chain, they are later reconciled with the main blockchain.
Notable examples of off-chain solutions include the Lightning Network and sidechains, both of which have gained popularity for their ability to provide fast and efficient transaction processing.
Lightning Network operates on top of the Bitcoin blockchain and enables users to create payment channels between each other for conducting transactions off-chain. Once the channel is closed, the final state of the transactions is then recorded onchain. This helps to alleviate congestion on the main blockchain and allows for quicker and more efficient transaction processing.
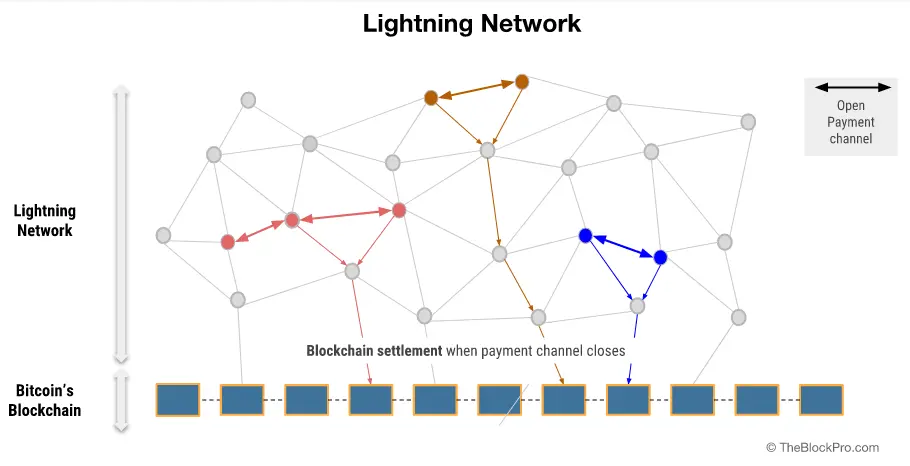
Improved Consensus Algorithms
The implementation of improved consensus algorithms is yet another method to address transactions that have not yet received confirmation. These algorithms are meticulously designed to optimize efficiency and minimize the time required for transactions to be confirmed.
By leveraging advanced consensus algorithms, the overall performance of the blockchain network can be enhanced, resulting in faster confirmation times and a more seamless transaction experience for users.
For example, if a new consensus algorithm allows for faster block times or larger block sizes, this can increase the throughput of the network and reduce the time it takes for transactions to be confirmed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, unconfirmed blockchain transaction, particularly in the Bitcoin network, can be a significant challenge for users, often resulting in delays and potential vulnerabilities such as double-spending. They may occur when a transaction is broadcast to the network but has not yet been added to a block. Factors contributing to pending transactions include network congestion, low fees, and transaction prioritization by miners.
To mitigate these issues, users can employ strategies such as paying higher transaction fees, efficient transaction replacement mechanisms like the Replace-by-Fee (RBF) protocol, and exploring off-chain solutions and layer 2 protocols. Additionally, the adoption of improved consensus algorithms can enhance the efficiency of the blockchain network, thereby reducing confirmation times and improving the overall transaction experience for users.
FAQ
Why Do Unconfirmed Transactions Happen in the Blockchain?
Unconfirmed transactions happen in the blockchain because they have not yet been included in a block. This can be due to network congestion, low transaction fees, or other factors. In this case, a payment will be in a pending state.
Can My Transaction Remain Stuck?
Yes, a transaction can remain stuck if it is not included in a block. This can happen if the transaction fee is too low or if the network is congested. If a transaction remains stuck for a long time, it may eventually be dropped from the mempool and will need to be re-broadcast to the network.
How to Cancel a Bitcoin Transaction if it is Unconfirmed?
It is not possible to cancel a BTC transaction once it has been broadcast to the network. However, you can use transaction replacement mechanisms to replace the unconfirmed transaction with a new transaction that has a higher fee. This is beneficial when there's a need to boost the transaction fee to guarantee its confirmation.
How Long Does a Bitcoin Transaction Take?
Several factors influence the duration required for a BTC transaction to receive confirmation, such as the transaction fee, the current state of network traffic, and the confirmation protocols employed by the wallet or exchange in question. In general, a transaction can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours to be confirmed. When there is a high volume of activity on the network or if the transaction fee set is insufficient, the confirmation of the transaction might experience delays.
*This communication is intended as strictly informational, and nothing herein constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy, sell, or retain any specific product, security or investment, or to utilise or refrain from utilising any particular service. The use of the products and services referred to herein may be subject to certain limitations in specific jurisdictions. This communication does not constitute and shall under no circumstances be deemed to constitute investment advice. This communication is not intended to constitute a public offering of securities within the meaning of any applicable legislation.




