Leverage Trading in Crypto: What is Crypto Leverage Trading & How It Works
What Is Leverage in Crypto Trading?
Leverage gives traders exposure to larger trading positions than they invest initially. It is also known as margin trading. This tool is used across traditional as well as cryptocurrency markets. While leveraged trading can multiply your profit, it can increase losses, too.
In this article, we will explain what cryptocurrency leveraged trading is and what type of leveraged positions there are. We'll also discuss the risks associated with leverage and how they can be mitigated.
Key Takeaways
- Leverage trading is increasing the size of the trading position;
- As much as leverage can increase your profit, it may increase losses, too;
Leverage Crypto Meaning
Why make a 10% profit with your limited capital, when you could make more profit with extended capital? Leverage trading helps a trader or investor make the most out of a correct market prediction. Unfortunately, it also has the same increased impact when the trade goes against your prediction.
Leverage trading increases your investment position size for increased profits, and it also leaves you vulnerable to huge losses. The maintenance threshold to which a trader can leverage a trade varies with different exchanges and has become attraction points used by brokerages to reel traders to their trading platforms.
How Does Leverage Trading Work in Crypto
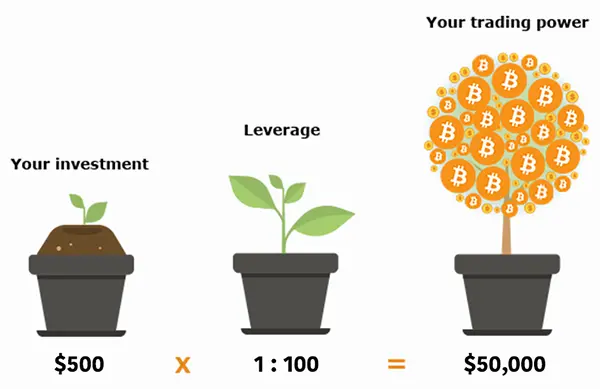
One important thing to note is that leverage trading works with ratios; 1:10, 1:50, 1:100, 1:500, up to 1:1000. What this means is, if you want to invest $1000 in a digital asset at a leverage of 1:100 (100x leverage), you will need to open a position with $100 only. A leveraged trade like this gives you a 10x potential profit and a 10x potential loss.
Opening a position in trading can either be long or short. So, if you believe a digital asset or assets will rise in value, you open long positions on them. The reverse is the case for short positions.
For example, in spot trading, going short on Bitcoin means borrowing Bitcoin, which you sell afterward. If the price drops, you buy the Bitcoin at a lower price, and then return the Bitcoin by selling it, and keeping the profits.
To open long positions on a leveraged trade, a trader must maintain an amount in his account as collateral. If his trade goes well, the broker returns his initial deposit plus profit. If the trade flops, the broker retains the money and liquidates the position. Proper risk management recommends you use lower leverage to reduce the chances of liquidation.
Leverage And Volatility In The Crypto Market
Does leverage create volatility in the crypto market? Questions around the impact of leverage and volatility in Bitcoin's market have been a focal point in crypto discussions, as few understand their relationship
There are a number of reasons why Bitcoin and several other blockchains are highly volatile, and among them is leverage. For example, Bitcoin's relative newness as an asset class is responsible for its continuous price discovery, which in turn causes volatility. Bitcoin's limited supply at 21 million without the possibility to be inflated is also a factor that contributes to its volatility.
The absence of a proper regulatory framework for blockchain technology makes it open to price manipulation and influence from whales and other capital-intensive institutions, which induces its own volatility.
What many don't know is that leverage, the excessive use of it by traders, is also responsible for volatility in Bitcoin's market. Using leverage increases the chances of liquidation, that is, a quick, brutal, and total loss of capital should the market go against your prediction. Because Bitcoin is a highly volatile asset, the excessive use of leverage by traders tends to liquidate a lot of accounts when the market goes against the highly leveraged bets.
This situation adds extra sell pressure on Bitcoin, because these traders hold collateral in it, and when their positions get liquidated their BTC gets sold. That is, of course, not true for sophisticated traders who reasonably hedge their positions or structure their bets in such a way that a sudden bear market won’t result in significant losses.
Leverage Trading Crypto Example
Let's look at a few examples of trading with leverage in detail.
Example of a Leveraged Long Position
For example, you assume that the price of an asset will go UP and therefore want to open a long position of $100,000 with 10x leverage. In this case, the margin will be $10,000. If the price of the asset goes up by 15%, the net profit will be $15,000, much higher than the profit of $1,500 without leverage.
If you made a wrong assumption and the price moves down 15%, the drop will liquidate your position. Prior to liquidation, the exchange will send a warning — margin call. By adding assets to your wallet and increasing your margin, you can avoid liquidation.
Example of a Leveraged Short Position
Now, imagine the opposite. You anticipate that the price of an asset will go DOWN and therefore want to open a short position of $100,000 with 10x leverage. In this case, you need to borrow the asset from another market participant and sell it at the current market price. The pledge will be $10,000. Since you are trading with 10 times leverage, you will be able to sell the asset for $100,000.
Let’s say the current price of the asset is $100,000. You decide to borrow and sell 1 unit of the asset. If you guessed the market movement and the price of the asset drops 15% (to $85,000), you can buy back 1 unit of the asset for $85,000. That would result in a net profit of $15,000.
In the event you made a wrong prediction and the price of the asset goes up 15% to $115,000, you would need to deposit another $15,000 to buy back 1 unit of the asset. The position will be liquidated if the balance reaches $1,000. To avoid liquidation, you need to deposit more funds until your position goes above the liquidation threshold.
Uses of Leverage in Crypto Trading
Traders combine the different amounts of investment and leverage ratio risk depending on their abilities. However, leverage is a great tool only when you are confident that the likelihood of a profit is higher than the likelihood of a loss.
Given the known market condition and high volatility of the blockchain network, you need to be extremely cautious and careful. Make sure to use technical and fundamental analysis before opening a position. Calculate the potential losses and decide if you can afford them.
Common Leverage Trading Instruments
The most adopted way of leveraging trades is through derivatives. Derivatives, in all simplicity, are an agreement between two parties or more, whose value is determined by an underlying financial asset.
Considering Bitcoin, Sam believes BTC will increase from $40k next week, and Jane believes BTC will drop to $30k from next week. They both enter into a contract that says, if BTC rises to $50k next week, Jane will pay $10k to Sam, and if BTC drops to $30k, Sam will also pay Jane $10k. This shows that derivatives allow a trader to profit both ways in the market, making it widely adopted by traders.
There are different types of derivatives contracts which include:
Bitcoin Futures: Bitcoin Options: This contract gives investors the option to buy or sell Bitcoin on a cryptocurrency exchange at a predetermined price and date. It is similar to a Futures' contract, only that they don't have to be triggered.
Bitcoin Options: This contract gives investors the option to buy or sell Bitcoin at a predetermined price and date. It is similar to a Futures' contract, only that they don’t have to be triggered.
Bitcoin Perpetuals: Perpetuals do not have a specific date or price limit. A trader can open a position for as long as he likes, so long as certain conditions are met.
How to Manage Risks with Leveraged Trading?
Leveraged trading is an extremely risky instrument, so it is important to limit risks as much as possible:
- First, assess your trading capabilities and risk tolerance. You should not trade with leverage on your last money (and without leverage, too);
- Use smaller leverage ratios. Trading with high leverage like 100x leverage requires less collateral, but increases the risk of liquidation; Understand your margin threshold and trade accordingly.
- Use risk management strategies such as stopping loss. This type of order limits your risks by automatically closing a trade under specified conditions. This is especially useful when the market moves not in your favor;
- Always monitor the margin level, even if your broker uses a margin call. If necessary, replenish your account or exit trades. Otherwise, not only can you lose all of your assets, but you can also remain in debt to your broker.
- If you are a beginner trader, you should try to stick to spot markets as the market volatility in the derivatives market can lead to the amplification of losses.
Cross margin or isolated margin
In trading, the margin is collateral for opening a leveraged position. On cryptocurrency exchanges, the margin can be allocated for each trade separately or for all trades together.
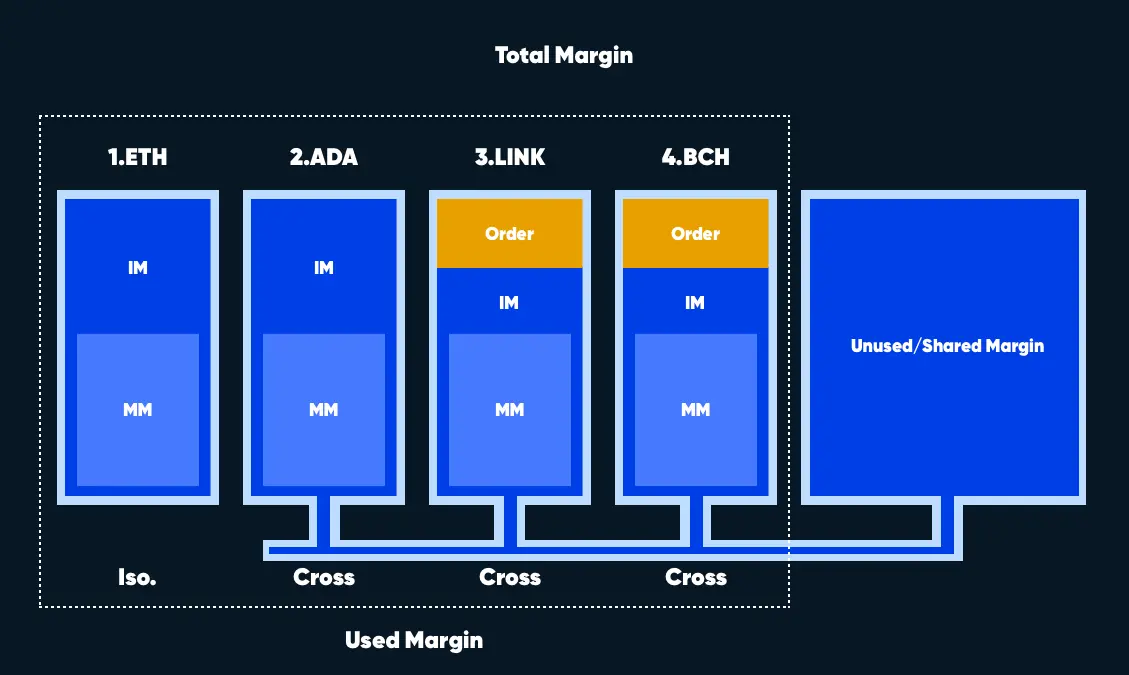
Cross margin is traditionally used in all financial markets. It is a kind of trading standard: the trader's entire deposit acts as collateral for all open positions. Thus, if the liquidation of the position happens, the trader will lose the entire deposit.
If a certain amount is allocated to a particular trade and only this amount is at stake, the such margin is called isolated. An isolated margin allows for managing risks in individual positions.
Liquidation and Margin Call
Margin Call is one of the exchange protection mechanisms. It is a broker’s warning to increase the collateral to avoid the position’s liquidation. Typically, a margin call comes in a form of a notification. In case you made a wrong forecast and the market moved in the opposite direction, your collateral may not be enough to cover losses. To prevent debts, the platform will liquidate your position. You have the option to either add more margin or accept the liquidation.
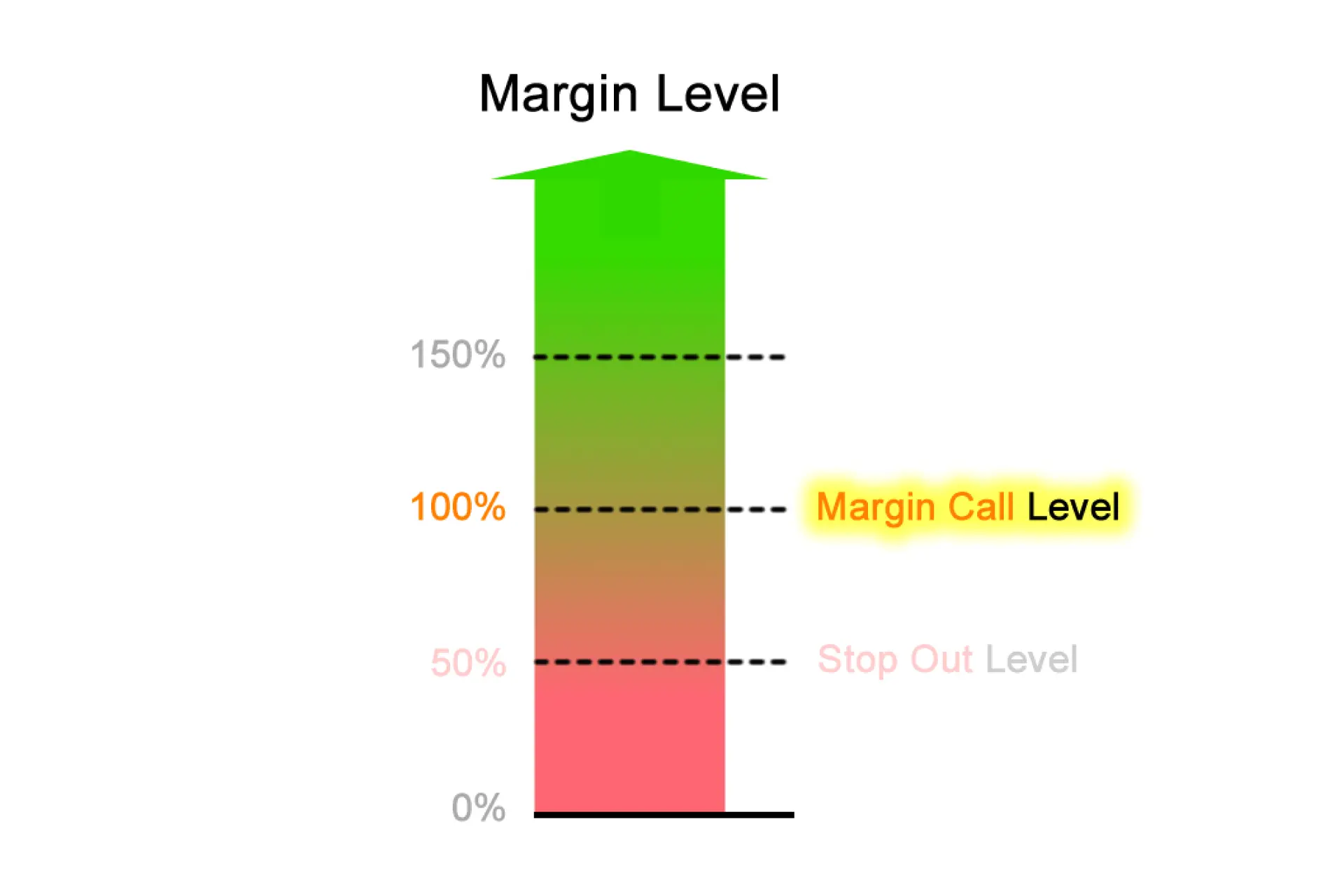
Before increasing the collateral, it is advisable to assess the market situation:
- If you anticipate a small correction with the price further going in your direction, in this case, it makes sense to add a margin to push the liquidation level lower;
- But in case you anticipate the market continuing to go against you, it is best to close your position immediately and lock in your losses.
When to Use Leverage in Crypto
Leverage can come in handy when you are certain of an opportunity on the market but do not have enough assets. A serious mistake would be to use this tool regularly merely out of greed. The best practice is to periodically incorporate leverage in your trading routine. It is recommended to trade with margin only after half a year of successful trading without positive saldo.
Cryptocurrency Margin Trading Strategies
Now you are aware of the idea of margin trading. So, what to do next? There are several strategies for margin trading. We'll look at them below.
Gradually Increase Trade Size
Start margin trading with a small deposit, gradually increasing the number of open positions. This allows you to gain the necessary experience without risking a lot of funds.
Practice Trading with Demo Trading
A demo account is a powerful tool for both beginners and experienced traders. It allows you to try out a wide variety of strategies, check commissions, and get acquainted with a new crypto exchange.
Set clearly defined goals and minimize risk
Before you start trading, make a plan of action. Having a plan is paramount in margin trading, because of a big risk factor. A clear understanding of the margin trading rules will help to build successful strategies. Strategy is exactly what separates professional trading from gambling.
Divide your Positions
Open trades on two or more independent trading accounts within one user account. Thus, the margin between accounts will be isolated, that is, a loss on one account will not lead to a change in the balance on the other.
Limit the time period of your trades
Limit open positions by time. Pre-determined length of larger position allows you to limit risks and avoid sudden negative market movements.
How Does Leverage Trading Impact Bitcoin Price?
Is the presence of leverage bad or good for the Bitcoin market? It might be easy to conclude it's bad, considering excessive leveraging was largely attributed to the May 2021 Bitcoin crash. But, it will also help to consider the role of leverage in crypto markets asides from volatility.
Leverage adds an important factor to the Bitcoin market, liquidity. And the presence of high liquidity in the market ensures efficiency in trade execution at specified prices, leading to a much improved price discovery for market makers. For instance, based on data gathered by TokenInsight across 42 exchanges, the crypto derivatives market had a trading volume of over $2 trillion in 2020.
Leverage trading in itself is healthy for the market, but the excessive use of it is what causes harm to the Bitcoin market. Where greed is curtailed, and effective risk management is used, leverage trading will continue to positively affect the Bitcoin market.
Pros & Cons of Leverage Trading Cryptocurrency
Bottom Line on What is Leverage in Crypto Trading
Being profitable involves knowing when to leverage and when not to. Fundamental understanding of the markets cannot be overemphasized, alongside meaningful market exposure, technical analysis, price movements, fundamental analysis, and sentimental analysis. Leverage trading is a popular choice in profitable financial instrument but can be costly if used wrongly and with larger exposure.
*This communication is intended as strictly informational, and nothing herein constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy, sell, or retain any specific product, security or investment, or to utilise or refrain from utilising any particular service. The use of the products and services referred to herein may be subject to certain limitations in specific jurisdictions. This communication does not constitute and shall under no circumstances be deemed to constitute investment advice. This communication is not intended to constitute a public offering of securities within the meaning of any applicable legislation.