Cryptocurrency Options Trading Guide: How To, Where, and Why
What Are Crypto Options: The Fundamentals
Options, like other derivatives, are simply contracts that permit investors or traders to make predictions about the future price of a cryptocurrency.
The crypto options market offers crypto traders the opportunity to buy or sell (write) options, enabling the trading of options on underlying assets.
Are There Options on Cryptocurrency at All
Yes. Options are popular among investors in the cryptocurrency sector because they may be used as a hedge against market risk, as a tool to offer wider market exposure (leverage), and for portfolio diversification.
How Crypto Options Differ from Traditional Markets
The major difference between options on cryptocurrencies and stocks is in how to buy them. Options in cryptocurrencies can be traded around the clock, while stock options can only be traded when the stock market is open. Volatility in the crypto market is also high, making premiums more expensive than those of the stock market.
Understanding Option 'Greeks'
Option Greeks are financial indicators of how sensitive the price of an option is to the factors that determine it, such as volatility or the value of the underlying asset.
Theta:
It is used to calculate an option's potential value loss per day as it approaches the expiration time.
Delta:
It helps to estimate how sensitive an option's price changes are comparable to the changes in the underlying asset’s price.
Gamma:
It refers to the potential change in the Delta if the crypto asset price changes.
Vega:
It is used for inferring how susceptible an option is to changes in implied volatility.
Why Are Crypto Derivatives Important?
Increasing Liquidity
Crypto derivatives constitute a significant factor in developing the cryptocurrency sector into a recognised asset class. Liquidity in the cryptocurrency markets rises as more traders trade options on crypto, enabling traders to conduct market transactions in the most cost-effective way possible.
Mitigating Risks
Derivatives help protect a portfolio from wildly fluctuating prices and unforeseen risks. A trader can bet on the decline of an asset's price by "shorting" it using derivatives like futures and options. A long-term investor with a portfolio of crypto assets can secure it against downturn markets with an options trading cryptocurrency strategy.
Portfolio Diversification
For several reasons, cryptocurrency derivatives are a crucial part of the crypto economy. First, using futures allows investors to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to various cryptocurrencies. Also, investors can develop complex trading techniques like hedging or arbitrage using derivatives.
Optimised Price Discovery
Another factor supporting the significance of derivatives is their optimisation of price discovery, which is the procedure for establishing an asset's value. Price discovery may become more effective with the ability of investors or traders to trade long and short, leading to more seamless market changes.
Purpose of Derivatives Trading in Crypto
Cryptocurrency derivatives can be used for
Hedging
The crypto market could sometimes go awry, leading to $billions in liquidations. With crypto derivatives, traders can hedge their long positions and reduce risk. This is particularly useful during corrections or bear markets. Instead of just passively waiting for the market reversal, traders can still make good use of their capital to reduce losses on their long positions.
Speculation
Apart from hedging, derivatives can come in handy in price speculation. Irrespective of the market's direction, any adept trader can make profits. Moreover, derivatives allow traders to profit off crypto volatility with leveraging. This way, traders get considerable exposure to the market with little capital. How to buy crypto options is note-worthy knowledge for every crypto trader.
Types of Crypto Options Available
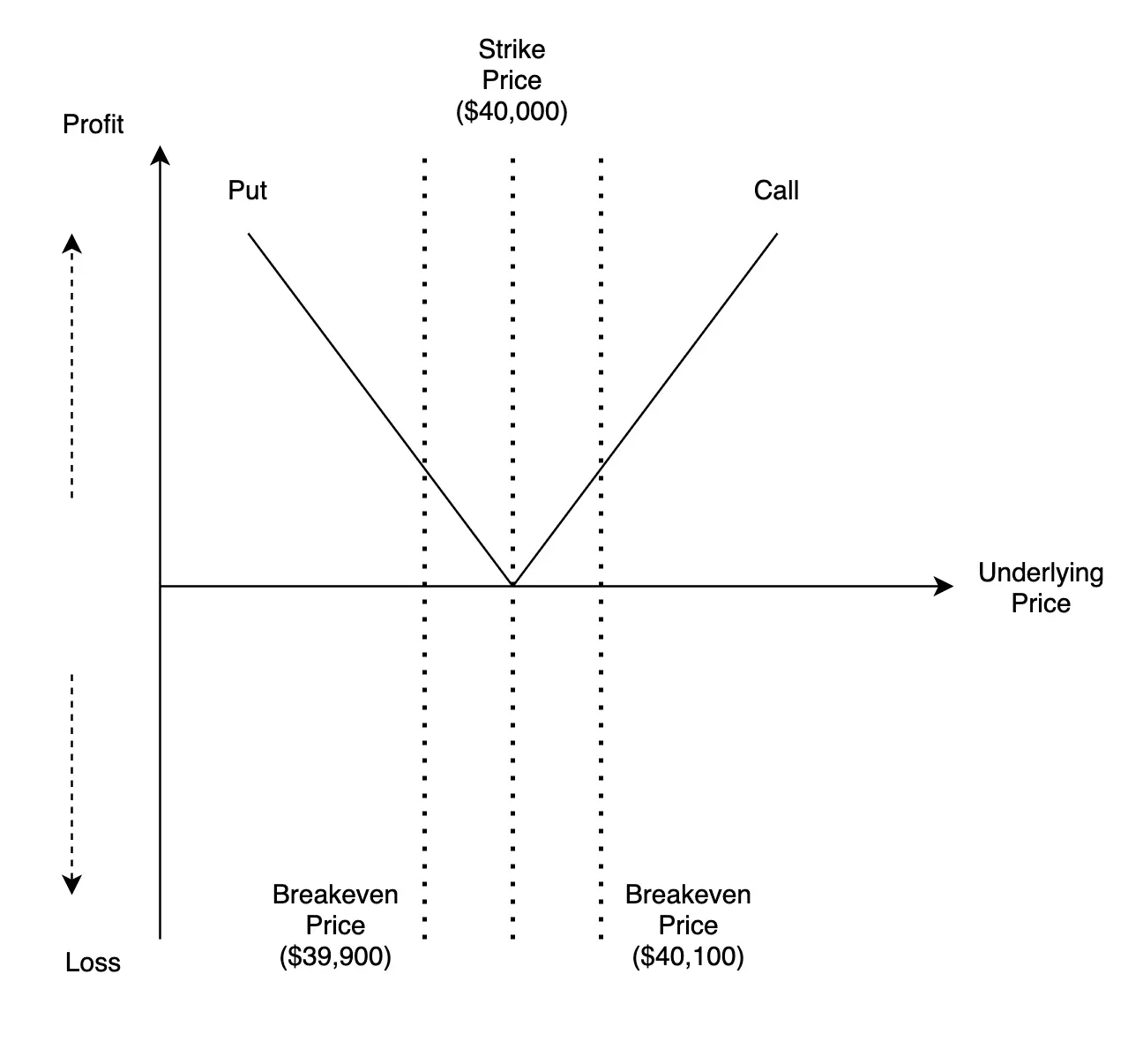
Call Options
A call option is a bet that the underlying asset's price will reach or not reach a higher price in a predetermined future. For the buyer, he is essentially saying the crypto’s price will be worth more than its strike price on a chosen date, while a seller believes it would be worth less than that price.
Buying Crypto Options
This strategy is employed when a buyer is bullish on a crypto price. The advantage it offers over buying directly an underlying asset is leverage trading. The higher the cryptocurrency from the strike price, the more the buyer will earn.
Buying Call Options: Example
For example, James buys a Bitcoin call option at a $37,000 strike price and June 2023 expiry. If he pays a premium (cost of buying the option) of $200 and the price of Bitcoin hits $50,000 at the expiry, he makes a $12,800 profit ($50,000-$37,000-$200).
Selling Call Options
For every cryptocurrency options buyer, there is a seller. When a trader sells (also called "writing") call option, he predicts that the price of the crypto asset will trade equal to, or lower than, the strike price (or that if the price exceeds strike it will still be less than the premium he receives upon selling the option). Selling calls is risky as the maximum losses are technically unlimited if the trade goes against the seller, even though they get to keep the premium.
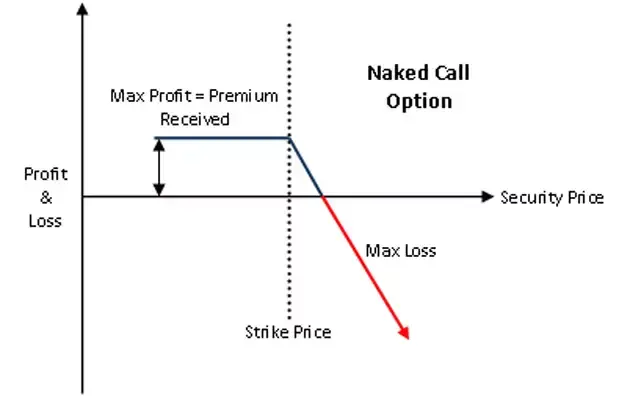
Selling Call Options - Example
James sells a December 20th call option of $35,000 strike price at a premium of $300. If the asset's price hits $35,000, James gets to keep the premium while there is no outstanding loss he needs to settle, so he made a maximum profit from the trade. This example shows us that the maximum profit from selling options (both calls and puts) is capped at the premium received.
What if the asset in our example hits $40,000 though? James then suffers a $(40,000 - 35,000 - 300) loss = $4,700.
Put Options
Buying Put Options
Just like call options, put options can be bought or sold. Purchasing a put option means a trader predicts the cryptocurrency price will decrease beyond a strike price at the expiry date. Selling a put option, on the other hand, is a prediction that the price of a crypto asset will not fall as deep as the strike price.
Buying Put Options: Example
For example, Maria owns ten Bitcoin with the current price of $50,000 per BTC. After several technical analyses, she predicts that Bitcoin will have a correction, and the price will fall to $37,000 within six months. Therefore, she buys a put option with a $46,000 strike price for a $2,300 premium. If her predictions come true and Bitcoin drops to $37,000 at the expiry (within the six months), Maria will make a $6,700 profit ($9,000 minus a $2,300 premium).
Selling Put Options
Everyone willing to buy an option on cryptocurrency must have a corresponding seller. A put seller's thoughts are that the cryptocurrency's price will either be at the strike price, above it, or not too much below the strike.
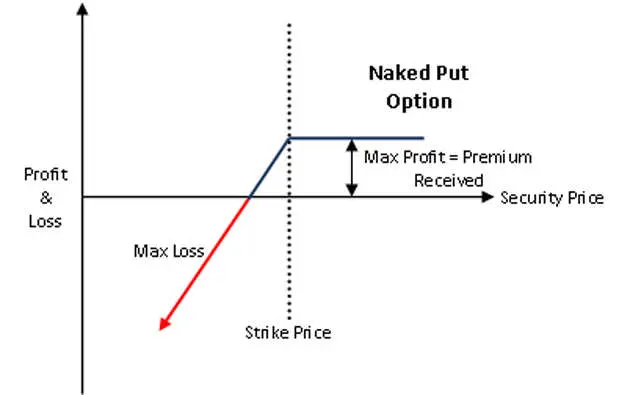
Selling Put Options - Example
Per the example used above, the trader who sold Maria a put option at a $46,000 strike price believes that the price of Bitcoin will be close to or above $46,000 within the next six months. If he is right, he can keep the $2,300 premium and his BTC. If he is wrong and the price drops beneath the strike, he keeps the $2,300 but is forced to pay Maria the difference between the strike and the market price.
Let's say BTC expiries at $45,000. This level is $1,000 less than the expiry, but since the seller received a $2,300 premium from Maria for selling her the option, the premium not only offsets a $1,000 loss but actually makes him net a $1,300 profit even though the BTC price at the expiry was less than the strike price.
American vs European
As regards exercising, crypto options can be grouped into two categories;
- European: contracts under the European style can only be exercised at the expiry.
- American: American contracts can be exercised anytime during the contract's validity.
Typically, American options are more expensive than their European counterpart given that they give more rights to the buyers. Interestingly, while the majority of the stock options market is in American options, European options contracts are highly prevalent in crypto options trading.
Inverse vs. USD-denominated Options
Options on cryptocurrencies can be grouped by the currencies they are quoted and settled in.
- USD-Denominated Options: Most exchanges quote options in their dollar value. They are mainly denominated in either dollars or stablecoins which some traders can find easier when calculating Profit and Loss. Settlement is then also made in dollar value.
- Inverse: The inverse options differ from the USD-denominated ones because while they are quoted in USD, they are settled in cryptocurrency. A Bitcoin option will be settled in BTC, and an Ethereum Option will be settled in ETH.
In The Money (ITM) vs Out of The Money (OTM)
Cryptocurrency options can be grouped into two categories depending on the market price and strike price.
- OTM: Out of the money is another name for “unprofitable”. For a call option, this scenario happens when the current price of the underlying crypto is less than the strike price. On the contrary, a put option is out of the money when the current crypto price is higher than the strike price.
- ITM: In the money refers to profitable options. An in the money call option means the current price of the underlying is higher than the strike price. Invariably, an in the money put option is when the current asset price is lower than the strike price.
Cash-Settled vs Physically-Settled
Cryptocurrency options can be settled in either of two ways; physically or with cash. The underlying coin is not physically delivered under the cash-settled form; settlement is made with cash, most often using US dollars or a stablecoin.
A physically settled crypto option, on the other hand, settles by actually delivering the underlying cryptocurrency. The terms on the deliverable of a crypto option contract are always predetermined.
Advantages of Crypto Options
Market Efficiency
Cryptocurrency option trading ensures the market's equilibrium and stability and the accuracy of the market values of the underlying assets due to the usage of arbitrage.
Low Transaction Costs
Cryptocurrency options trading fees are typically much less than fees pertaining to spot trading. This, coupled with leverage trading, makes for much greater capital efficiency of options trading when compared to trading directly in the underlying.
Risk Management
Derivative contract values are inextricably linked to the underlying assets. Derivatives are therefore utilised to reduce the risks brought on by changing prices of the underlying assets.
For instance, the investor may be able to compensate for his losses on spot trading with the gains from derivatives. In the event that he shorts via derivative contract and the value of the underlying asset declines, the losses from the spot are offset by the gains from the short position.
Higher Leverage
As one of the derivative contracts, the crypto option enables traders to increase profit margins through leverage without having to make a substantial initial investment.
High Liquidity
The options markets are particularly liquid due to the high demand for derivatives trading. In fact, typically, the derivatives markets are substantially more liquid than spot markets, with this trend already imprinted on crypto too.
Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency Options
Higher Risk
Due to the frequent value fluctuations of the underlying assets, derivatives can be pretty volatile. Investors thus risk losing money, especially when using leverage.
Regulatory Concerns
The use of derivatives might still be prohibited in various parts of the world. As a result, for two parties to enter into a contract, they must reside in jurisdictions where derivatives contracts are lawful.
Lack of Due Diligence
The lack of due diligence in over-the-counter futures contracts exposes investors to counterparty risks. Since over-the-counter transactions don't always follow tight compliance guidelines, the trader can potentially lose funds due to counterparty risk. This risk is mitigated when using a derivatives exchange with appropriate onboarding procedures, a robust risk module, and sufficient margin requirements.
Cryptocurrency Options Trading Strategies
Bull Put Spread
The bull put spread is typically employed when asset prices have significantly fallen. In the market condition where this strategy pays off, put premiums are high, there is a lot of volatility, and the expiry date is far. There is also an expected slight bullish movement for this strategy to be most effective.
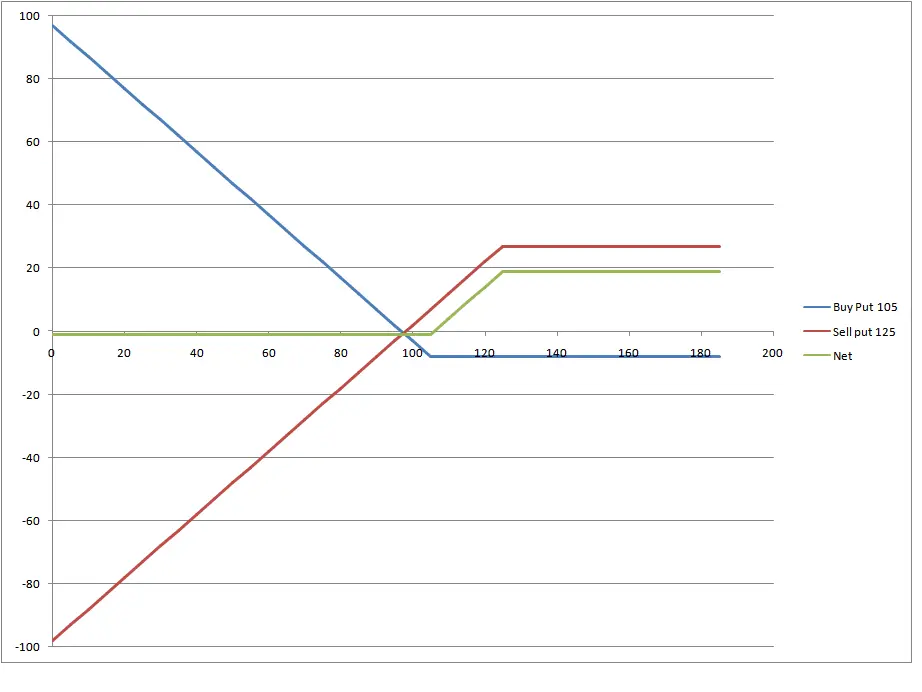
The bull put spread aims at benefiting from premium while limiting the risk of losses by creating a spread on put options.
How Does the Bull Put Spread Work?
- You buy an OTM (out of the money) put option.
- You sell an ITM (in the money) put option.
Although the bear put spread is not compulsorily created by buying an OTM and selling an ITM option, the choice of strike price depends on the aggressiveness of the trade.
The major thing to note for both options on cryptocurrency in the bull put spread is that the contracts should have the same number of options, pertain to the same underlying asset, and have the same expiry date.
Bull Put Spread Example
Outlook – Moderately bullish (expect the market to remain neutral or go slightly higher)
Bitcoin – $20,005
Bull Put Spread trade set up –
- Buy the $19,000 put option by paying $923 as a premium; do note this is an OTM option.
- Sell the $22,000 put option and receive $2,507 as a premium; note this is an ITM option.
- The net cash flow is the difference between the debit and credit, i.e. $2,507 – $923= $1,584 (net credit)
Let’s now look at different scenarios at expiry.
Scenario 1 – Market expires at $18,000 (below the lower strike price, originally OTM option)
The value of the put options at expiry depends upon their intrinsic value. The inherent value of a put option upon expiry is
Strike – Spot
In the case of the $19,000 put option, the intrinsic value would be –
$19,000 – $18,000
=$1,000
Since we are long on the $19,000 put option by paying a premium of $923, we would make:
= intrinsic value – premium paid
= $1,000 – $923
= $77
Likewise, in the case of the $22,000 put option, it has an intrinsic value of $5,000, but since we have sold/written this option at $2,507, the payoff from $22,000 would be
$2,507 – $4,000
= – $1,493
Overall strategy payoff would be –
+ $77 – $1,493
= – $1,416
Scenario 2 – Market expires at $19,000 (at the lower strike price, originally the OTM option)
The $19,000 put option will not have any intrinsic value. Hence, we will lose the premium we have paid, i.e. $923.
The $22,000 put option’s intrinsic value will be $3,000.
The net Payoff from the strategy would be
premium received from selling the $22,000 put option – intrinsic value of $22,000 put option – premium lost on $20,000 put option
= $2,507 – $3,000 – $923
= – $1,416
Scenario 3 – Market expires at $23,000 (above the higher strike price, originally ITM option)
The intrinsic value of both $19000 and $22,000 would be $0. Hence both the options would expire worthlessly.
Net Payoff from the strategy would be –
premium received for $22,000 – premium Paip for $20,000
= $2,507 – $923
= + $1584
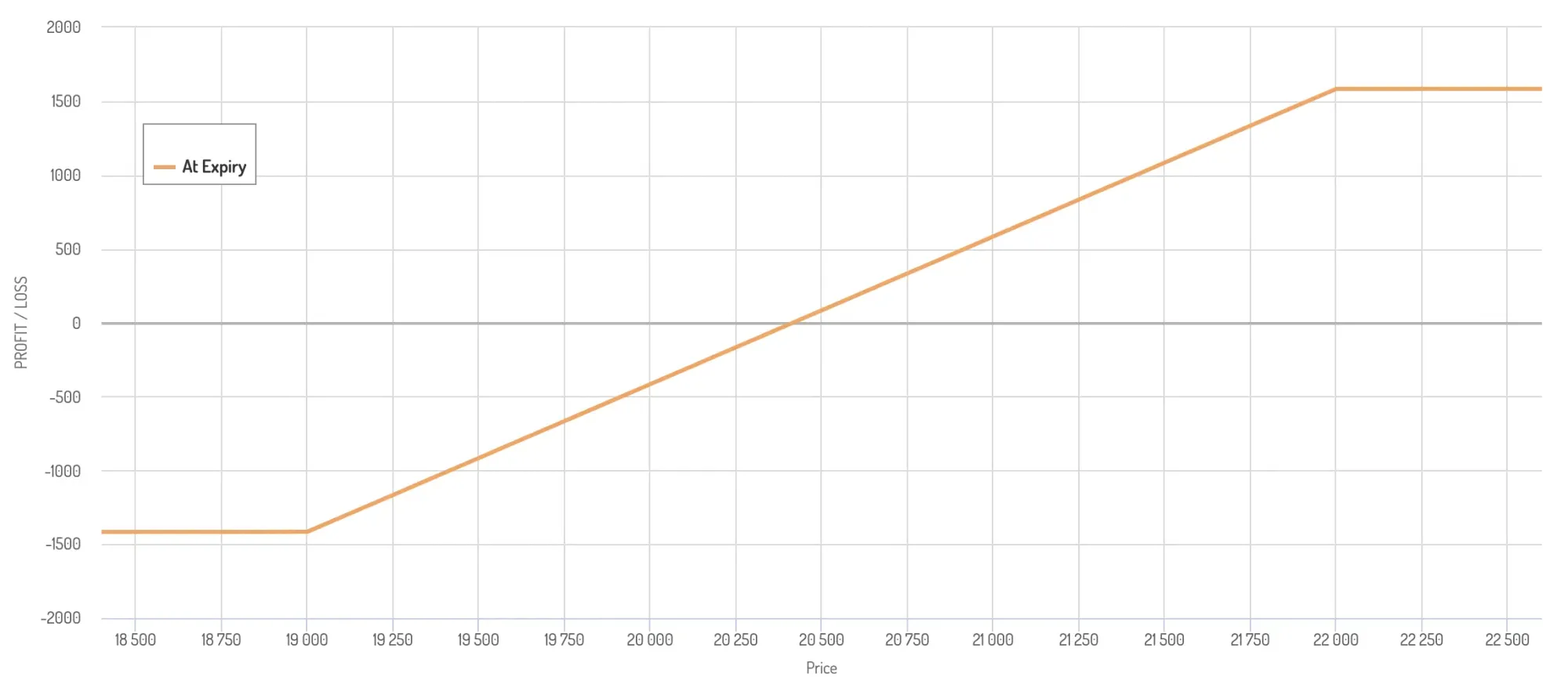
Both the graph and the 3 scenarios above illustrate how a moderately positive market move contributes to the highest gains when deploying a bull put spread strategy.
Bear Put Spread
The bear put spread is employed when asset prices are expected to slightly decrease. In this strategy, the gain is limited, as is the loss.
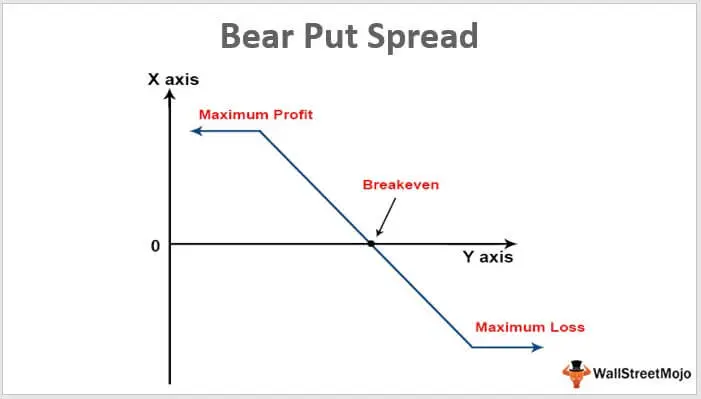
How does the bear put spread work?
- You buy an ITM put option.
- You sell an OTM put option.
- Both options should have the same expiry date, number of options, and underlying asset.
It's important to note that the bear put spread is not compulsorily created by buying an ITM and selling an OTM option. The important part is that it is created using two options. The choice of the strike depends on the aggressiveness of the trade.
Bear Put Spread Example
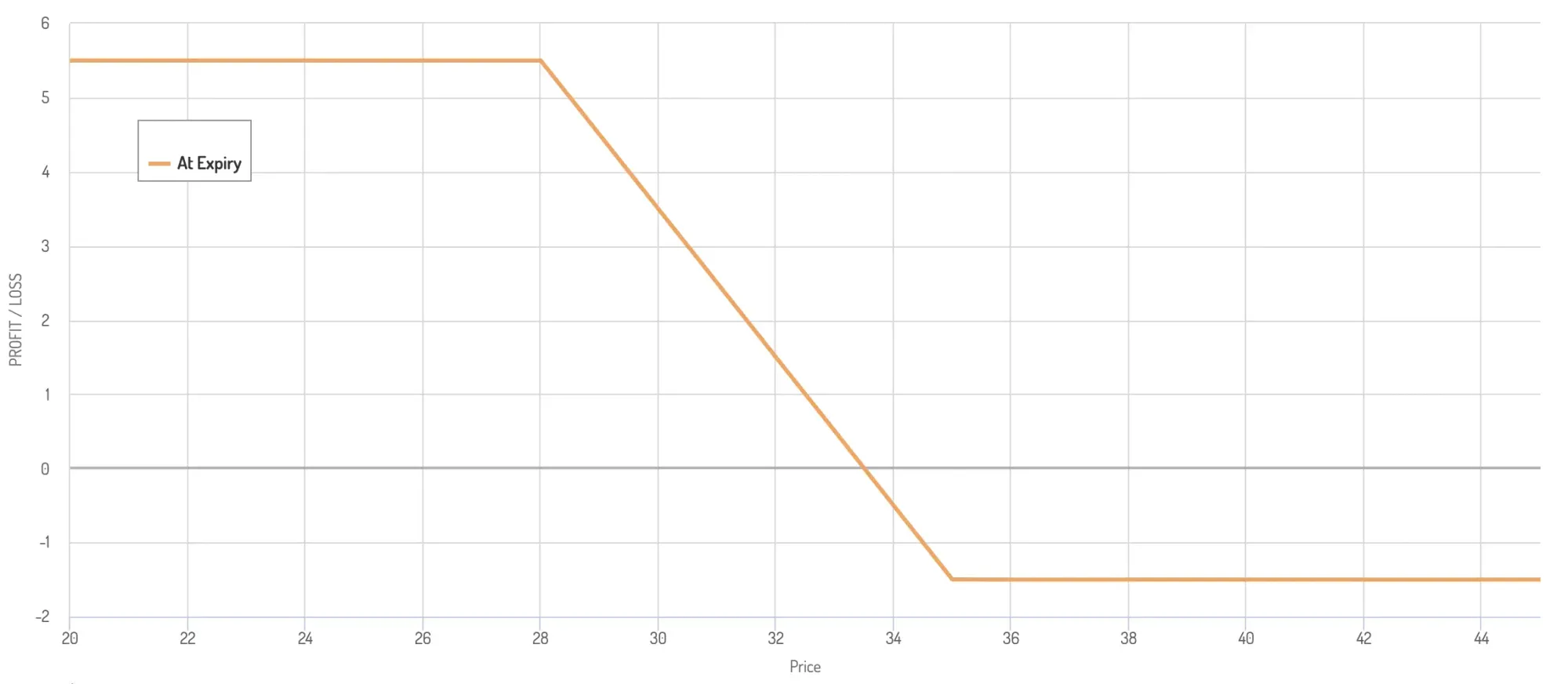
SOL's current price - $31
Buy a $35 ITM put option (pay $4 premium)
Sell a $28 OTM put option (earn a $2.5 premium)
Net credit = premium received minus premium paid = -$1.5 (means it's a net debit position)
Let’s see different scenarios for this strategy.
Scenario 1 – Market expires at $40 (above long put option)
In this case, the market has gone against our prediction,
- The premium paid for $35, i.e. $4, would go to $0; hence we make nothing
- The premium received for selling $28, i.e. $2.5, would be retained entirely while there would be no outstanding settlement payment to the buyer since the option doesn't have intrinsic value
- The overall loss would be equal to the net debit: $2.5 - $4 = – $1.5.
Scenario 2 – Market expires at $35 (at long put option)
In this scenario, we assume the market expires at $35, where we have purchased a put option. In this case, both the $35 option and $28 option would expire worthless (similar to scenario 1), resulting in a loss of $1.5.
Scenario 3 – Market expires at $28 (at short put option)
This is an exciting level. Recall that when we initiated the position, the spot was at $31, and now the market has gone down as expected. At this point, both options would have interesting outcomes.
- The $35 option would have an intrinsic value equivalent to $35 - $28 = $7. Since we paid a premium of $4 to purchase this option, the bottom line would be $7 - $4 = $3
- The $28 option would expire at the money (close or exactly at the strike price), hence the entire premium of $2.5 would be retained
- The net profit from the trade would be $3 + $1.5 = $5.5.
The net payoff from the strategy is in line with the overall expectation from the strategy, i.e. the trader gets to make a profit when the market goes down.
Scenario 4 – Market expires at 20 (below the short put option)
This is again an interesting level as both options would have an intrinsic value. Let's figure out how the numbers add up –
- The $35 option would have an intrinsic value equivalent to $35 – $20, which is $15. We have paid a premium of $4, which would be offset from the intrinsic value of $15, hence after compensating for the premium paid one would retain $11
- The $28 option would have an intrinsic value equivalent to $28 – $20, which is $8. Despite that received a premium of $2.5 for the option, we will still bear a loss of $1.5 - $8 = - $5.5
- On the one hand, we make a profit of $11, and on the other, we lose $5.5; therefore, the net payoff of the strategy would be $11 – $5.5 = $5.5.
Iron Condor
The iron condor is an options strategy that helps users profit off neutral markets (when there is minimal volatility). It uses four options, with the primary aim that all four options expire irrelevantly. Not to be mistaken with the normal condor, the iron condor uses both put and call options in one strategy (the normal condor uses either all call options or all put options).
The maximum gain from the iron condor is the premium received for selling options, while the maximum loss is seen when both call and put options sold end in the money and the call and put options bought end worthless.
Iron Condor Example
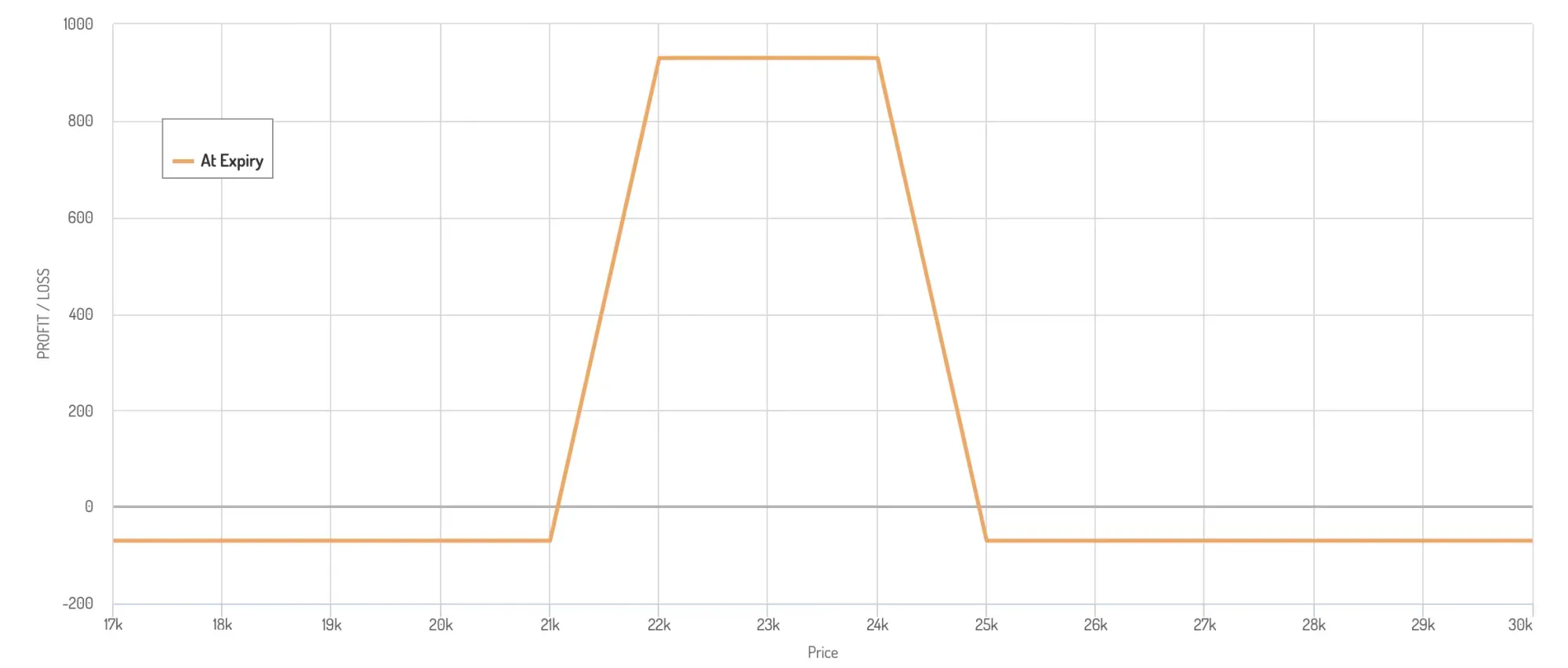
James sees the price of Bitcoin remaining relatively unhinged from its $23,000 price in the next month. He can use the iron condor to make the most of this asset’s flatness. He decides to sell a $24,000 call option and earn $1,200 as a premium. He then buys a $25,000 call option at a $962 premium. His net credit here is $238.
This is just one part of the iron condor. The other part makes him sell a $22,000 put option and earn $3,811 in premium. He will then buy a $21,000 put option at $3,119. The net credit here is $692.
His total net credit will be $930 ($1,200 - $962 + $3,811 - $3,119).
Let’s now see how the strategy develops across different scenarios.
Scenario 1
Bitcoin price remains within the $24,000 and $22,000 range, and all the options expire valuelessly; his profit will be the net credit received =$930. This is the desired outcome resulting in the maximum profit possible.
Scenario 2
Bitcoin price goes down to $21,500
$25,000 Call option bought = expires OTM (he loses $962 premium )
$24,000 Call option sold = expires OTM (he gains a $1,200 premium)
$21,000 Put option bought = expires OTM (he loses $3,119 premium)
$22,000 Put option sold = expires ITM (he loses $3,811 - $500 = $3,311)
The bottom line is -$962 + $1,200 - $3,119 +$3,311 = $430
Scenario 3
Bitcoin price drops to $20,000
$25,000 Call option bought = expires OTM (he loses $962 premium )
$24,000 Call option sold = expires OTM (he gains a $1,200 premium)
$21,000 Put option bought = expires ITM (he loses $21,000 - $20,000 - $3,119 premium = - $2,119)
$22,000 Put option sold = expires ITM (he gains $22,000 - $20,000 + $3,811 = $1,811 premium)
The bottom line is - $962 + $1,200 - $2,119 + $1,811 = - $70
Scenario 4
Bitcoin rises to $24,500
$25,000 Call option bought = expires OTM (he loses $962 premium )
$24,000 Call option sold = expires ITM (he gains $24,000 - $24,500 + $1,200 premium = $700)
$21,000 Put option bought = expires OTM (he loses $3,119 premium)
$22,000 Put option sold = expires OTM (he gains $3,811 premium)
The bottom line is - $962 + $700 - $3,119 + $3,811 = $430
Scenario 5
Bitcoin rises to $26,000
$25,000 Call option bought = expires ITM ( he gains $26,000 - $25,000 - $962 premium) = $38
$24,000 Call option sold = expires ITM (he loses $24,000 – $26,000 + $1,200 premium = -$800)
$21,000 Put option bought = expires OTM (he loses $3,119 premium)
$22,000 Put option sold = expires OTM (he gains $3,811 premium)
The bottom line is $38 - $800 - $3,119 + $3,811 = - $70
Selling 'Naked' Call And Put Options
Oftentimes, when a trader sells an option because the losses are unlimited, they buy/sell the cryptocurrency to mitigate losses (a process called delta hedging). When a trader does not own the underlying cryptocurrency, he is selling a naked option.
If a trader sells (writes) naked calls, it means the trader doesn’t own the underlying asset. If the asset rises above the strike prices, the losses could be disastrous. Likewise, a trader selling naked puts predicts the price of the asset will not drop past a strike price by not having bought the necessary collateral to settle the trade should the market go against them. Naked selling can be prevented by proper risk management and collateral requirements outlined by a crypto exchange.
Covered vs Uncovered Options
Naked positions, described above, are also called “Uncovered”. On the contrary, the covered option is when you can trade options while holding the underlying asset. This way, depending on the position, you can mitigate the losses when the bet goes against you and have the necessary collateral to cover the losses.
Managing Risk With Options
Conservative investors can use options in crypto as a way to hedge very volatile periods. Instead of selling your cryptocurrencies when the market does not seem favourable, you can say buy put options, and if the crypto price doesn’t fall, you only lose your premium. If it does fall though, you get to keep your asset and can either exercise your contract or sell your option for a profit, mitigating the losses incurred on the underlying.
Options Margin
An options margin refers to the collateral deployed when writing and maintaining an option. Buyers taking up a long position do not need to put up margin, but sellers writing options need margin to enter and sustain their position.
Unified Margin and Portfolio Margin
A portfolio margin is a way of determining the margin requirements of a crypto options position by using all relevant positions to offset the risk and calculate the net margin.
A unified margin account is a feature on crypto options trading platforms that allows users to share the same margin across multiple subaccounts while offsetting the P/L across those accounts. Several trading instruments such as spot, margin, futures, perpetual swaps, and options can be taken into account. Unified margin doesn't only apply to different trading instruments but also different assets, meaning that a trader is able to trade say ETH options while holding collateral only in BTC.
Where to Trade Crypto Options?
Can you buy options on cryptocurrencies? Yes. Below are some of the most popular cryptocurrency options trading platforms.
OKEx
Options in crypto are one of the derivatives products offered by OKEx. The exchange offers options contracts on Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Solana. The crypto options platform uses a contract multiplier of 0.1 for its Bitcoin contracts, meaning every Bitcoin options contract bought represents 0.1 BTC.
Deribit
Deribit became one of the best crypto options exchanges pioneering the crypto options market, hence attracting a huge majority of open interest. Its platform is reliable and robust allowing institutional players to plug in via API while providing retail investors with an easy-to-use interface to trade cryptocurrency options.
Bit
Bit is a Seychelles-based company featuring several derivatives contracts like futures and options. Although it might not be as popular as the other exchanges on our list, its relative ease to trade crypto options makes it a favorite platform for some traders.
Features To Look For in Crypto Options Trading Platform
Insurance Funds
Every derivative platform needs an Insurance fund. This aspect is important when avoiding losses during times of market turmoils in case exchanges' risk engines fail and traders lose more than they have.
Several crypto options trading platforms choose to run multiple insurances as the crypto market has shown it can go overboard with volatility.
Auto Deleveraging
Oftentimes, the movement from crypto prices may be so sharp that insurance is unable to cover the liquidation losses. In this case, an exchange may be forced to auto deleverage. This means the leverage positions for other users are reduced to clever the cost of leveraging for that one user. There might be several features put in place to avoid this, and they must be put into consideration before choosing an exchange to trade your derivatives.
Stop Loss and Take Profit
These two order types allow a trader to automatically reduce losses and make profits when the market conditions are met. Suppose a market goes against you until it reaches the level where you set up a stop loss order. At that moment, the stop loss gets triggered and executed as a market order to close your position. Take profit works the same way just in an opposite direction when the market goes your way and you are to capture the profit.
Partial Close Orders
Would you want to lock in some of your profits? Some derivative exchanges allow you to take some profit off the board. This term is known as partial close orders. Traders remove some profit while still keeping certain exposure to the market.
Advantages Over Other Derivatives
- Options offer a limited risk profile if structured properly.
- Options can be combined into different strategies depending on traders’ investment profiles.
Crypto Options Alternatives
Crypto Options vs Stock Options
- The major difference between options in cryptocurrencies and stocks is that crypto options can be traded round the clock, while stock options can only be traded when the stock market is open.
- Volatility in the crypto market is typically high, making premiums more expensive than those of the stock market.
Options vs Futures
Both options and futures are the two most popular derivative types, but they are inherently different. Options offer a more extensive variety of trading strategies and a more limited risk profile for options buyers. Options essentially provide exposure to volatility trading while futures use tends to be rather directional.
Options vs Perpetuals
The main difference between options and perpetual futures is in the expiration date. Perpetual futures have no expiration date, while options on crypto must be exercised at a certain time.
Final Considerations
The options on crypto market is growing in popularity as it offers traders the ability to make predictions about the future prices of cryptocurrency assets and trade the volatility. As the crypto options market grows, more and more people are likely to take advantage of their knowledge of the cryptocurrency volatility markets. We hope this piece has helped clarify how to trade crypto options.
FAQ
Can You Trade Options on Cryptocurrency?
Yes. Like traditional assets, cryptocurrency options can be bought or written (sold).
How Popular Are The Crypto Options?
Cryptocurrency options are popular among both retail and institutional traders with the open interest gradually growing.
What Other Things Do I Need to Consider Before Joining a Crypto Options Trading Platform
There are a few other things you should consider apart from the requirements listed in the article.
- Is the exchange legal in the country you are domiciled in?
- If you are a newbie trader, does the exchange have features to aid your trading?
- How much liquidity does the exchange have?
Can Beginners Use Derivative Exchanges?
Yes. Although crypto derivatives can be difficult to navigate, they are open to all. Just a quick piece of advice - try your hand at easier crypto features before diving into derivatives trading.
I Still Don’t Get It; Can the Bitcoin Futures and Options Be Explained In Simple Terms?
Imagine there is a piece of land on sale next to your house. Options trading in crypto can be likened to you meeting the seller and paying a token to purchase the house at the current price at a later date. If the value of the house goes up, you pay at the agreed price. If it goes down, you can decide against the purchase and the seller keeps the token paid. If you had a futures contract to buy the house, you wouldn’t have a possibility to turn down the purchase if the price went down and you would end up owning the house regardless.
What Are The Types of Bitcoin Derivatives?
There are four types of derivatives contracts; futures, perpetual swaps, options, and CFDs.
*This communication is intended as strictly informational, and nothing herein constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy, sell, or retain any specific product, security or investment, or to utilise or refrain from utilising any particular service. The use of the products and services referred to herein may be subject to certain limitations in specific jurisdictions. This communication does not constitute and shall under no circumstances be deemed to constitute investment advice. This communication is not intended to constitute a public offering of securities within the meaning of any applicable legislation.