Credit Spreads in Options Trading: Definition, Strategies, and Examples
Credit spread is a fairly popular strategy among risk-averse option traders. In this piece, we will take an in-depth look at the usage of credit spreads in cryptocurrency options trading. Read on to learn how to trade credit spreads, their pros and cons, and trading examples.
Key Takeaways:
- Credit spread is an option strategy consisting of two call or put options with different strike prices.
- Bull put credit spread includes a short put with a higher strike and a long put with a lower strike.
- Bear call credit spread includes a short call with a lower strike and a long call with a higher strike.
- As the names of the strategies suggests, bull put spread is for bullish traders, and bear call spread is for bearish traders.
Understanding a Credit Spread Option
Before getting into the specifics of the strategy, let’s briefly go over the concept of option spread. A spread is the simultaneous purchase and sale of options of the same class (calls or puts) and with the same underlying asset, but with different strike prices. In this article, we will discuss a vertical spread, which consists of options with the same expiration. Credit spread essentially falls under the category of vertical spreads.
What is a Credit Spread Option?
Depending on which class of options is included in the strategy, the credit spread can have either a bullish or a bearish bias. Hence, there are two types of credit spreads: bull put credit spreads and bear call credit spreads.
Why Trade Credit Spreads?
First and foremost, credit spreads are popular as they provide an opportunity to generate profit from the difference in premiums in a limited-risk fashion. The strategy is typically employed to capture moderate underlying moves of the underlying cryptocurrency price.
Credit spread strategies also require much less capital than many other trading strategies and are flexible to use under different market conditions.
What Are the Types of Credit Spreads?
Depending on which class of options is included in the strategy, the credit spread can have either a bullish or a bearish bias. Hence, there are two types of credit spreads: bull put credit spreads and bear call credit spreads.
Pros and Cons of Credit Spreads
Pros
Pros of a credit spread strategy in options:
- Limiting potential losses. The credit spread gives you the opportunity to generate income with limited risk.
- Flexibility. The trader can customize the strategy to fit his risk profile.
- Possibility to profit in a low volatility environment.
Cons
Cons of credit spread strategy in options:
- Credit spreads have limited profit potential.
- Risk of insufficient protection. Although maximum losses are limited, a trader can still lose a large portion of their investment if the asset price goes in the wrong direction.
- Credit spreads are also subject to certain risks, such as time decay and volatility. Misjudging these factors can lead to an unfavorable outcome.
Bull Put Credit Spread

If the trader is bullish, they can implement the bull put credit spread. Let’s look at its components:
- Sell put option with a higher strike.
- Buy put option with a lower strike.
Because the option with a higher strike will be more expensive than the one with a lower strike, this spread will result in an initial credit.
As it’s a bull strategy, its key goal is to take advantage of the increase in the price of the underlying asset before the expiry of the options. As a result, you will not have to deliver the asset of the sold option.
Market Outlook
Typically, one will have a bullish directional bias to enter the bull put credit spread strategy. The undesirable outcome for this strategy is a strong drop in the price of the underlying cryptocurrency, which can cause the trader to lose money.
How to Set up
To set up a bull put credit spread strategy, you need to:
- Select an asset;
- Determine the magnitude of the expected bullish forecast;
- Choose a target price — this is important as the point of maximum profitability is at or above the short strike;
- Determine the position size.
The risk of the position will be limited to the width of the spread minus the credit received. And the breakeven price is the strike price of the short option minus the credit received for its sale.
At the same time, the maximum profit for the strategy is limited to the credit received for selling the credit spread put option minus the credit paid for buying the put option.
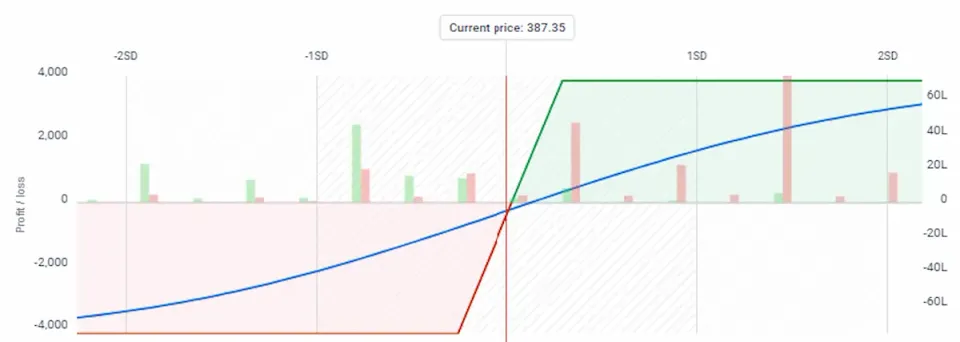
Payoff Diagram
For the bull put credit spread strategy, the payoff chart will look like this:

The X-axis on the chart shows the price of the underlying asset, and the Y-axis shows the profit or loss. The line on the graph shows how the profit or loss for this strategy will change depending on the price of the underlying cryptocurrency at the time of expiration of the options.
Entering
As it was mentioned earlier, to implement the strategy, a trader sells a put option with a higher strike and buys a put option with a lower strike with the same expiration date.
That said, there are some nuances to consider prior to implementing the bull put spread. On the one hand, the larger the spread size, the greater the net credit, and therefore the greater your potential maximum profit. However, the potential risk increases, too. As the distance between the options' strike prices increases, the long option cannot effectively protect itself against a drop in the price of the asset.
Exiting
There are two reasons to exit a trade: when one’s market forecast has been met or when it has changed. The original position can be simply liquidated by executing the reverse position. In the case of a bull put spread, it can be liquidated with a bear put spread.
Sometimes liquidity issues arise in liquidating the original spread. The choice would be then to employ the synthetically equivalent bear call spread to close the trade.
Time Decay Impact
Time Decay (Theta) is a favorable factor for the bull put credit spread strategy because it affects the reduction of the premium on the sold option. This means that the trader will gain more profit when the position is closed. However, if the price of the underlying asset begins to fall and gets closer to the strike price level, time decay can become a disadvantage and lead to an increase in potential losses
Implied Volatility Impact
Implied volatility (IV) affects the bull put credit spread strategy as follows:
- If the IV decreases after opening a position: positive impact because the value of the options decreases, and you can close the position with more profit;
- If the IV increases after the position is opened: negative impact because the value of the options increases, which can lead to big losses when you close the position.
It is important to note that when implied volatility changes, the impact on each of the call options in the spread can be different because options with different strikes and expiration dates have different sensitivity to volatility.
Adjusting
The bull put credit spread strategy can be adjusted or modified to create a different options trading strategy. For example, a trader can include additional options, change the strike prices, or option expirations to modify the risk and potential profit of their position.
One adjustment option could be to add a call option with a higher strike price level to create an iron condor strategy. This strategy is a combination of bull put credit spread and bear call credit spread. It is used to protect the position from moves in both directions of the asset price.
Rolling
If the trader's prediction turns out to be incorrect and the cryptocurrency makes a short-term bearish move, a rollover can be used. This is a method of position regulation in options trading, which often involves moving an option to a later expiration date. An example would be closing the current position and opening a new position with a later option expiration date and lower option strike prices to extend the options' life and protect the position from potential losses.
Hedging
This strategy can be hedged in various ways. One way is to apply dynamic hedging, where you regularly adjust your position in the market of the underlying asset (buy or sell it) to reduce the impact of adverse price changes on your bull put credit spread strategy. However, this will require you to actively monitor the market and be prepared for transactions in the underlying asset.
Bear Call Credit Spread

Alternatively to the bull put spread, the bear call spread can be implemented if the trader is bearish. The strategy consists of two call options:
- Sell a call option at a lower strike price.
- Buy a call option at a higher strike price.
Because the call with the higher strike will be less expensive than the call with the lower strike, the spread will result in an initial credit.
If the price of the asset remains below the short option strike at the time of expiration of the options, both options will not be exercised. In this case, the trader receives the maximum profit, equal to the received net credit. Meanwhile, the time decay and reduction of implied volatility can also bring additional benefits to the trader.
Market Outlook
Ideally, you should have a moderate bearish forecast for using the bear call credit spread strategy. Thus, the options will remain out of the money and will not be exercised, allowing the trader to maximize profits.
How to Set up
In general, to set up a bear call credit spread strategy, just like with the bull put credit spread, you need to select an asset, contract size, and two call options with different strike prices and expiration dates. It is also important to have an idea of the target price, which should be at or below the short strike for a bear spread.
Payoff Diagram
The payoff chart for the bear call credit spread strategy will look like this:

The X axis on the chart shows the price of the underlying asset, and the Y axis shows the profit or loss. The line on the graph shows how the profit or loss of this strategy will change when the price of the underlying asset changes at the time of the expiration of the options.
Entering
To enter a Bear Call Credit Spread position, the trader must sell (write) a call option with a lower strike price and buy a call option with a higher strike price.
As with the bull put spread, the key factors that determine profit and risk for the bear call spread are the following:
- The size of the spread;
- The distance between the strike price of the short option and the current asset price.
Exiting
The bear call spread can be liquidated by executing the reverse position: a bull call spread. Alternatively, in case of liquidity issues, a synthetically equivalent spread may be used to close the position — a bull put spread.
Time Decay Impact
Time decay (Theta) is a favorable factor for the bear call credit spread strategy because it affects the decrease in the premium on the sold option. This means that the trader will make more profit when closing the position. However, if the price of the underlying asset begins to rise and approaches the strike price level, time decay can become a disadvantage and lead to increased potential losses if the trader decides to close the position early.
Implied Volatility Impact
Implied volatility (IV) affects the bear call credit spread strategy in the same way as the bull put credit spread strategy. A decrease in IV after the bear call credit spread opens is favorable, and an increase in IV is unfavorable.
Adjusting
An adjustment to the bear call credit spread strategy may be required if the price of the asset begins to move upwards, approaching the strike price of the sold call option. For example, the trader can close the position and lock in a profit if the asset price is approaching the strike price of the sold call option. This would also help to reduce the potential loss in case the price of the asset increases further.
Rolling
Rolling a bear call credit spread strategy involves closing the current position and opening a new position with a higher strike price and a later expiration date. As one way to adjust the strategy, rolling can be used if the price of the asset begins to move up and approach the strike price of the sold call option.
Hedging
Bear call credit spread hedging strategies incorporate a variety of tools and strategies.
For example, you can use the calendar spread by selling longer-term call options with the same strike as the options in your bear call credit spread strategy. This can provide an additional premium that compensates for potential losses if the market moves against your expectations.
Keep in mind, however, that while reducing risks, hedging can also reduce potential profits.
Trading Examples
Bull Put Credit Spread Trading Example
Here is an example of a bull put credit spread strategy where the underlying cryptocurrency is Bitcoin with a current price of $20,000. To implement the strategy, the trader needs to:
- Sell (short) a put option with a higher strike, in this case $18,000, receiving a premium of, for example, $500.
- Buy a (long) put option with a lower strike, in this case $15,000, paying a premium of e.g. $200.
Both options must have the same expiration date.
Maximum profit is equal to the difference between the premiums: $500 (received) – $200 (paid) = $300
If Bitcoin remains stable or rises in value, both options will expire worthless, and the trader will keep the premium received. If Bitcoin falls below the strike of the sold put option ($18,000), the potential profit will decrease. The maximum loss will be the difference between the two strikes ($18,000 – $15,000 = $3,000) minus the premium received.
Bear Call Credit Spread Trading Example
Here is an example of the bear call credit spread strategy, where the underlying asset is Bitcoin, with a current price of $20,000. To implement the strategy, the trader must:
- Sell (short) a call option with a lower strike, in this case, $22,000, receiving a premium of, for example, $500.
- Buy a (long) call option with a higher strike, in this case, $25,000, receiving a premium of, for example, $200.
Both options must have the same expiration date.
The trader's maximum profit is the difference between the premiums: $500 (received) – $200 (paid) = $300
If Bitcoin remains stable or declines in value, both options will expire worthless, and the trader will keep the premium received. If Bitcoin rises above the strike of the sold call option ($22,000), the trader's potential profit will decrease. The maximum loss will be the difference between the two strikes ($25,000 – $22,000 = $3,000) minus the premium received.

Best Credit Spread Strategies
Basically, there are several basic strategies that use credit spreads. In addition to the bull put credit spread and bear call credit spread we discussed earlier, there is also the iron condor and butterfly spread.
All four strategies use credit spreads and allow investors to earn a premium in different market conditions: bullish, bearish, or neutral.
FAQs
What Is A Credit Spread In Options Trading?
A credit spread is a strategy that consists of two call/put options with distinct strike prices. One option is sold, and another is bought. The difference in premiums of the two options leaves the trader with the net credit, which is the maximum potential profit for the strategy.
Is Debit Spread Better Than Credit?
Debit and credit spreads have their advantages and disadvantages, and neither is inherently better than the other.
Can You Lose Money Trading Credit Spreads?
Yes, traders can lose money trading credit spreads, but only partially. Credit spreads have limited profit potential but also limited loss potential. Traders should weigh the risks carefully before entering into a trade.
Can You Make a Living Selling Credit Spreads?
It is possible to make a living selling credit spreads, but it requires skill, experience, and discipline. Traders should carefully plan their trades and manage their risk exposure to be successful over the long term.
*This communication is intended as strictly informational, and nothing herein constitutes an offer or a recommendation to buy, sell, or retain any specific product, security or investment or to utilise or refrain from utilising any particular service. The use of the products and services referred to herein may be subject to certain limitations in specific jurisdictions. This communication does not constitute and shall under no circumstances be deemed to constitute investment advice. This communication is not intended to constitute a public offering of securities within the meaning of any applicable legislation.